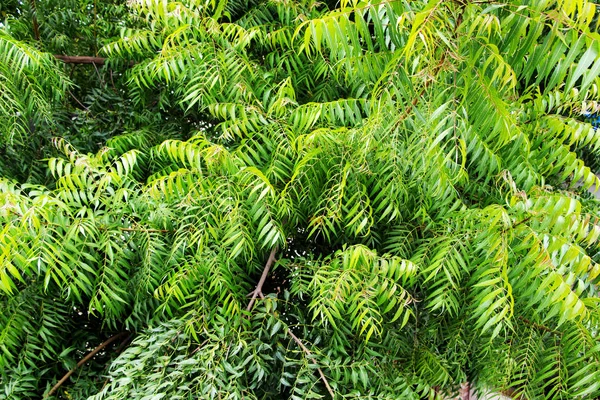
Azadirachta indica
Azadirachta indica, commonly known as neem, margosa, nimtree or Indian lilac, is a tree in the mahogany family Meliaceae. It is one of two species in the genus Azadirachta. It is native to the Indian subcontinent and to parts of Southeast Asia, but is naturalized and grown around the world in tropical and subtropical areas. Its fruits and seeds are the source of neem oil. Nim is a Hindustani noun derived from Sanskrit nimba. Neem is a fast-growing tree that can reach a height of 15–20 metres (49–66 ft), and rarely 35–40 m (115–131 ft). It is evergreen, shedding many of its leaves during the dry winter months. The branches are wide and spreading. The fairly dense crown is roundish and may reach a diameter of 20–25 m (66–82 ft). The opposite, pinnate leaves are 20–40 cm (8–16 in) long, with 20 to 30 medium to dark green leaflets about 3–8 cm (1+1⁄4–3+1⁄4 in) long. The terminal leaflet often is missing. The petioles are short.

Azadirachta indica
The Neem tree (Azadirachta indica) is a tropical evergreen tree native to India and Southeast Asia.

Azadirachta indica
The first recorded use of Neem for medicinal purposes dates back to ancient Indian texts such as the

Cassia Fistula
Despite its beauty, the tree is highly toxic, with all parts of the plant containing the toxin cytisine. Ingestion of the plant can cause severe symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, and convulsions. The golden shower tree is a medium-sized tree, growing to 10–20 m (33–66 ft) tall with fast growth. The leaves are deciduous, 15–60 cm (6–24 in) long, and pinnate with three to eight pairs of leaflets, each leaflet 7–21 cm (3–8 in) long and 4–9 cm (1+1⁄2–3+1⁄2 in) broad.The flowers are produced in pendulous racemes 20–40 cm (8–16 in) long, each flower 4–7 cm (1+5⁄8–2+3⁄4 in) diameter with five yellow petals of equal size and shape. The fruit is a legume, 30–60 cm (12–24 in) long and 1.5–2.5 cm (9⁄16–1 in) broad, with a pungent odor and containing several seeds.

Azadirachta indica
Neem (Azadirachta indica) is a member of the Meliaceae family and its role as health-promoting effect is attributed because it is rich source of antioxidant. It has been widely used in Chinese, Ayurvedic, and Unani medicines worldwide especially in Indian Subcontinent in the treatment and prevention of various diseases. Earlier finding confirmed that neem and its constituents play role in the scavenging of free radical generation and prevention of disease pathogenesis. The studies based on animal model established that neem and its chief constituents play pivotal role in anticancer management through the modulation of various molecular pathways including p53, pTEN, NF-κB, PI3K/Akt, Bcl-2, and VEGF.

Azadirachta indica
Neem trees can reach 15–30 metres (49–98 feet) in height and have attractive rounded crowns and thick furrowed bark. The compound leaves have toothed leaflets and are typically evergreen but do drop during periods of extreme drought. The small fragrant white flowers are bisexual or staminate (male) and are borne in clusters in the axils of the leaves. The fruit is a smooth yellow-green drupe and has a sweet-flavoured pulp.
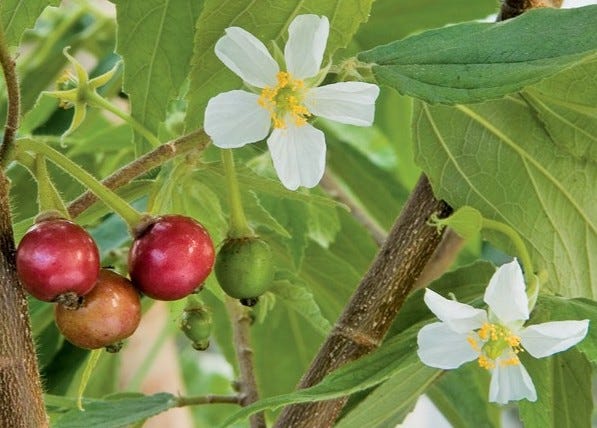

Mutinga Calabura
Muntingia is a genus of plants in the family Muntingiaceae, comprising only one species, Muntingia calabura, and was named in honour of Abraham Munting. It is native to the Neotropics, from Mexico south to Bolivia and Argentina, with edible fruit, and has been widely introduced in other tropical areas. Muntingia calabura is a shrub or tree that grows fast up between 7.5 to 12 m tall with spreading branches.[4] The leaves are alternate, distichous, oblong or lanceolate, 4–15 cm long and 1–6 cm wide, with toothed margin and covered in short hairs. The flowers are small (up to 3 cm wide), solitary or in inflorescences of two or three flowers, with five lanceolate sepals, hairy, five obovate white petals, many stamens with yellow anthers, and a smooth ovoid ovary. The flowers last only one day, their petals drop in the afternoon.
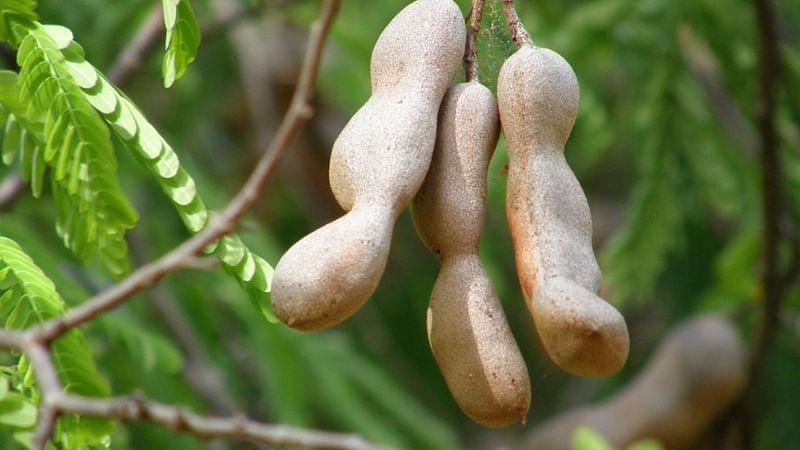

Tamarindus indica
Tamarind (Tamarindus indica) is a leguminous tree bearing edible fruit that is indigenous to tropical Africa and naturalized in Asia. The genus Tamarindus is monotypic, meaning that it contains only this species. It belongs to the family Fabaceae. The tamarind tree produces brown, pod-like fruits that contain a sweet, tangy pulp, which is used in cuisines around the world. The pulp is also used in traditional medicine and as a metal polish. The tree's wood can be used for woodworking and tamarind seed oil can be extracted from the seeds. Tamarind's tender young leaves are used in South Indian and Filipino cuisine. Because tamarind has multiple uses, it is cultivated around the world in tropical and subtropical zones.

Millingtonia hortensis
The tree grows to a height of between 18 and 25 metres and has a spread of 7 to 11 metres. It reaches maturity between 6 and 8 years of age and lives for up to 40 years. It is a versatile tree which can grow in various soil types and climates with a preference for moist climates. Like Nyctanthes arbor-tristis, it blooms in night and sheds during morning. Flowers give very pleasant smell. The white flowers come as large panicles which emit a pleasant fragrance. They are bisexual and zygomorphic. The bell-shaped sepals of the flower have five small lobes. The flower has four stamens with parallel anthers unlike in most other plants of this family where the anthers are divergent. The corolla is a long tube with five lobes.

Delonix regia
Delonix regia is a medium-sized deciduous tree that grows to about 10 m (33 ft). The bark is light brown. Often creased at branches, it has prominent lenticels. The flowers are large, with four spreading scarlet or orange-red petals up to 8 cm (3 in) long, and a fifth upright petal called the standard, which is slightly larger and spotted with yellow and white. They appear in corymbs along and at the ends of branches. The naturally occurring variety flavida (Bengali: Radhachura) has yellow flowers. The pods are green and flaccid when young, then turn dark-brown and woody as they mature. They can be up to 60 cm (24 in) long and 5 cm (2 in) wide. The seeds are small, weighing around 0.4 grams (6.2 grains) on average. The compound (doubly pinnate) leaves have a feathery appearance and are a characteristic light, bright green. Each leaf is 30–50 cm (12–20 in) long with 20 to 40 pairs of primary leaflets or pinnae, each divided into 10–20 pairs of secondary leaflets or pinnules. Pollen...
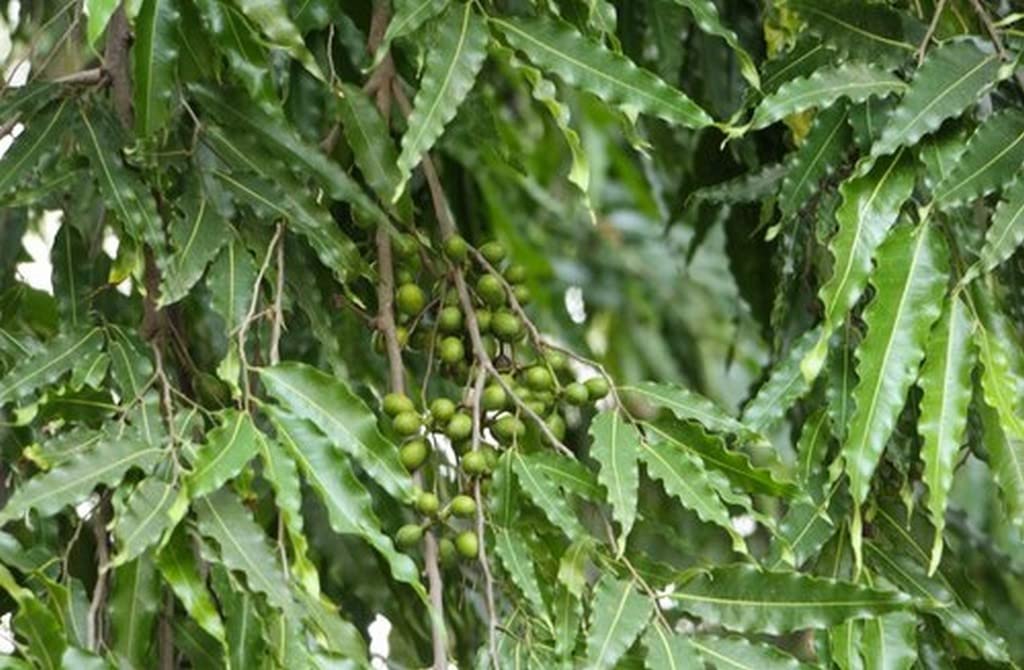

Polyalthia longifolia
Monoon longifolium, the false ashoka, also commonly known by its synonym Polyalthia longifolia, is an Asian small tree species in the family Annonaceae. It is native to southern India and Sri Lanka, but has been widely introduced elsewhere in tropical Asia. This evergreen tree is known to grow over 20 m. in height and is commonly planted due to its effectiveness in alleviating noise pollution. It exhibits symmetrical pyramidal growth with willowy weeping pendulous branches and long narrow lanceolate leaves with undulate margins. Monoon longifolium is sometimes incorrectly identified as the ashoka tree (Saraca indica) because of the close resemblance of both trees. The cultivated, column-like pendula form can appear to have no branches, but in fact a non-hybrid M. longifolium allowed to grow naturally (without trimming the branches out for decorative reasons) grows into a normal large tree giving plenty of shade.
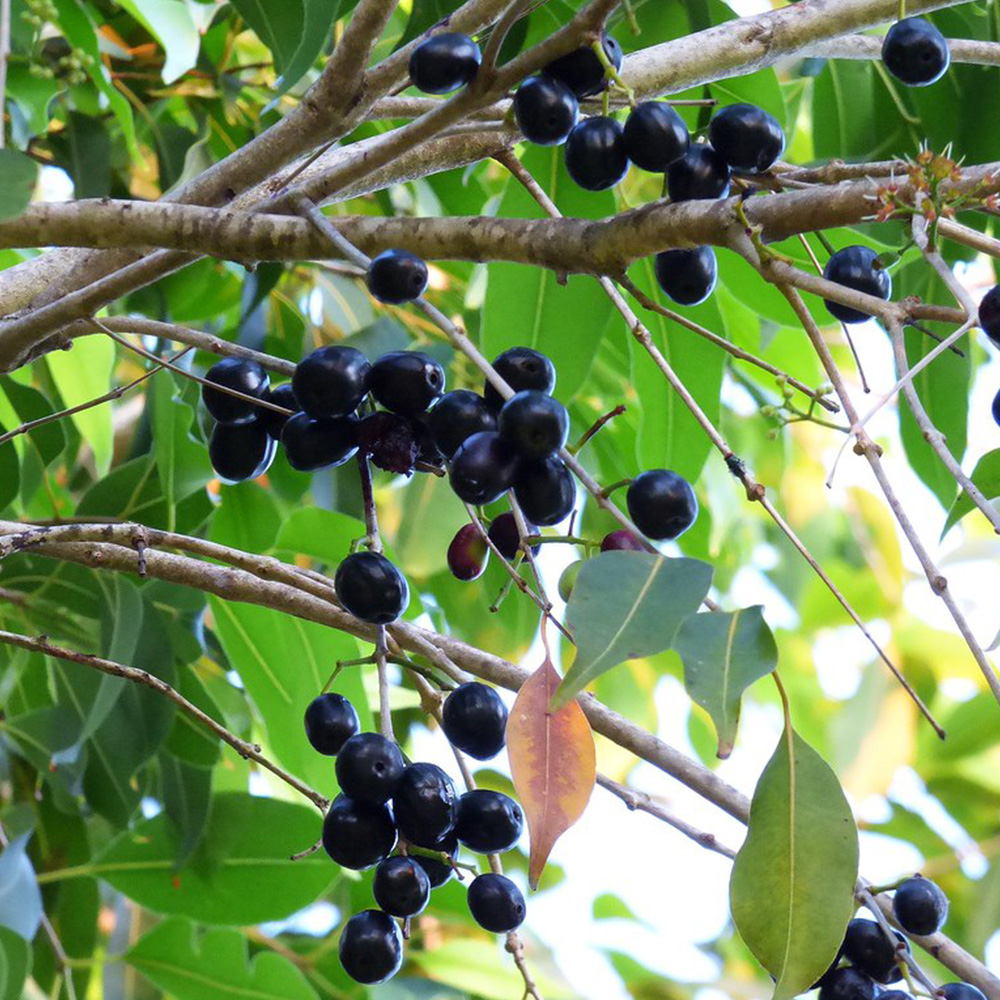

Syzygium cumini
As a rapidly growing species, it can reach heights of up to 30 m (100 ft) and can live more than 100 years. Its dense foliage provides shade and is grown just for its ornamental value. At the base of the tree, the bark is rough and dark grey, becoming lighter grey and smoother higher up. The wood is water resistant after being kiln-dried. Because of this, it is used in railway sleepers and to install motors in wells. It is sometimes used to make cheap furniture and village dwellings, though it is relatively hard for carpentry. The aromatic leaves are pinkish when young, changing to a leathery, glossy dark green with a yellow midrib as they mature. The leaves are used as food for livestock, as they have good nutritional value. Syzygium cumini trees start flowering from March to April. The flowers are fragrant and small, about 5 mm (0.2 in) in diameter. The fruits develop by May or June and resemble large berries; the fruit of Syzygium species is described as "drupaceous".[8] The fr...
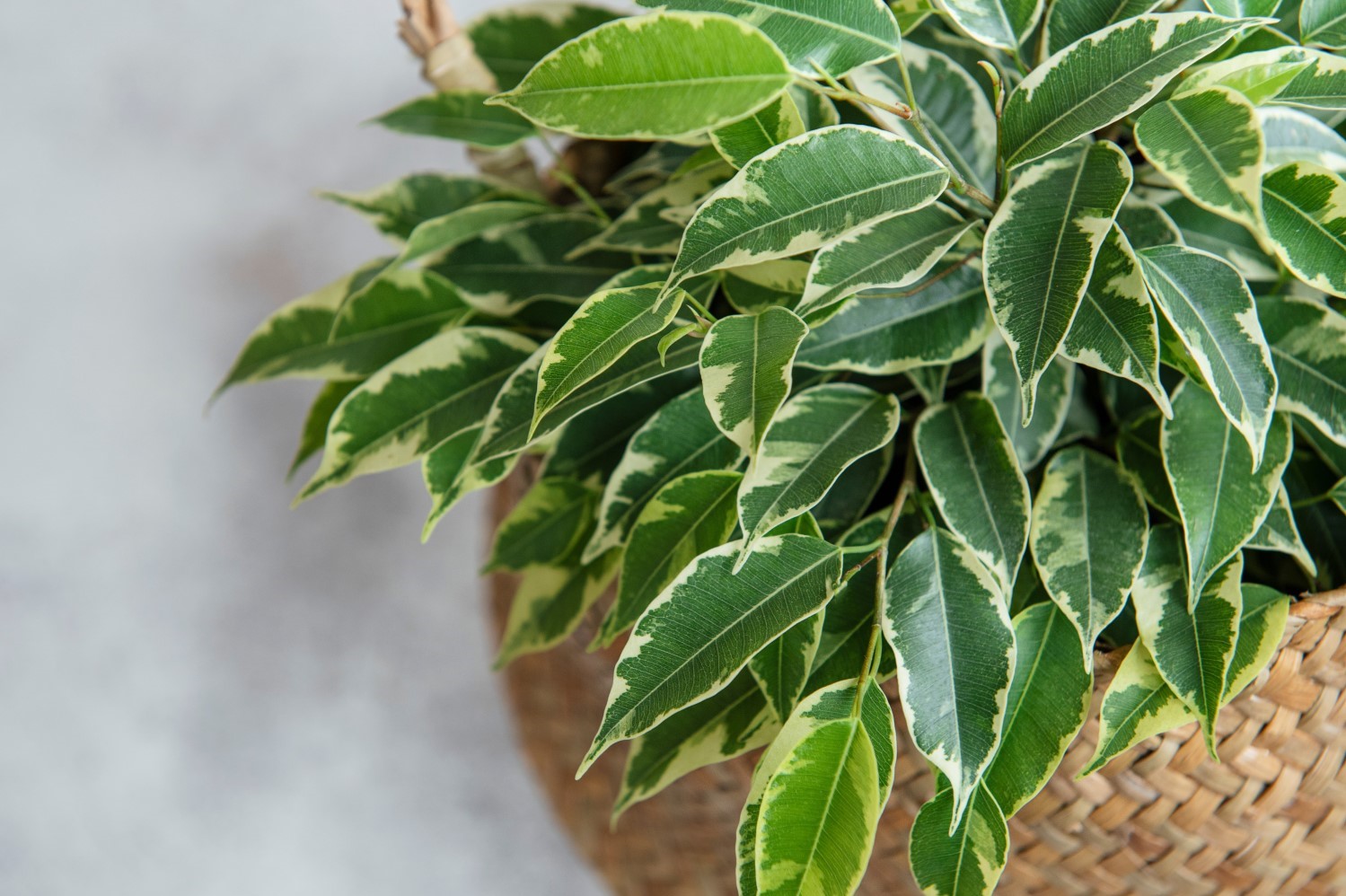

Ficus benjamina
Ficus benjamina, commonly known as weeping fig, benjamin fig or ficus tree, and often sold in stores as just ficus, is a species of flowering plant in the family Moraceae, native to Asia and Australia. It is the official tree of Bangkok. The species is also naturalized in the West Indies and in the states of Florida and Arizona in the United States. It is one of the most common trees in Israeli cities and parks. In its native range, its small fruit are favored by some birds.Ficus benjamina is a tree reaching 30 m (98 feet) tall in natural conditions, with gracefully drooping branchlets and glossy leaves 6–13 cm (2+3⁄8–5+1⁄8 inches), oval with an acuminate tip. The bark is light gray and smooth. The bark of young branches is brownish. The widely spread, highly branching tree top often covers a diameter of 10 meters. It is a relatively small-leaved fig. The changeable leaves are simple, entire and stalked. The petiole is 1 to 2.5 cm (3⁄8 to 1 inch) long.
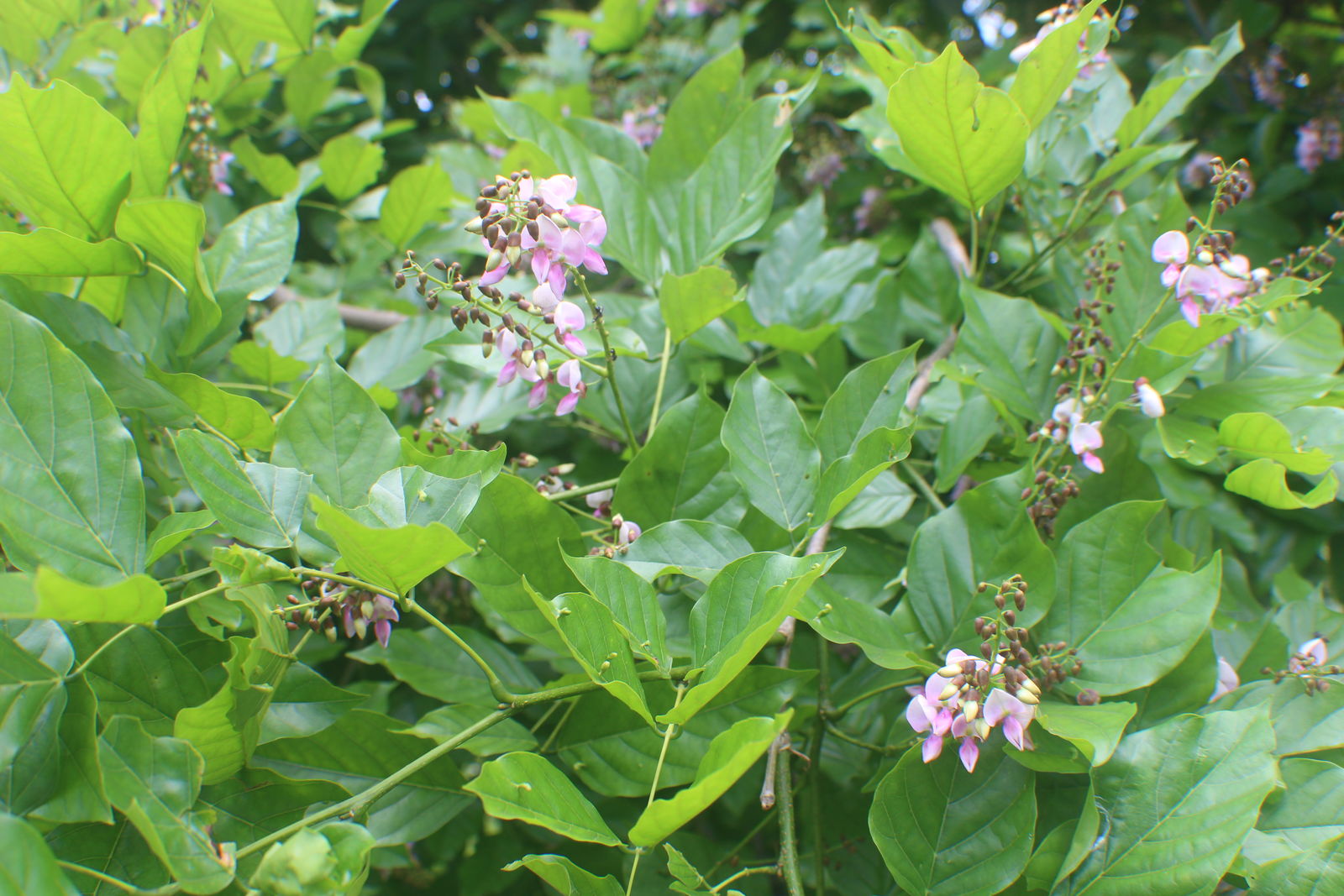

Millettia pinnata
Millettia pinnata, also known as Pongamia pinnata, is a tree species that belongs to the family Fabaceae. It is native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, but has been introduced to other parts of the world, including Africa and the Americas. Pongamia pinnata is a legume tree that grows to about 15–25 m (50–80 ft) in height with a large canopy that spreads equally wide. It may be deciduous for short periods. It has a straight or crooked trunk, 50–80 cm (20–30 in) in diameter, with grey-brown bark, which is smooth or vertically fissured. Its wood is white colored. Branches are glabrous with pale stipulate scars. The imparipinnate leaves of the tree alternate and are short-stalked, rounded, or cuneate at the base, ovate or oblong along the length, obtuse-acuminate at the apex, and not toothed on the edges. They are a soft, shiny burgundy when young, and mature to a glossy, deep green as the season progresses, with prominent veins underneath.

Terminalia catappa
Terminalia catappa is a large tropical tree in the leadwood tree family, Combretaceae, native to Asia, Australia, the Pacific, Madagascar and Seychelles. Common names in English include country almond, Indian almond, Malabar almond, sea almond, tropical almond, beach almond and false kamani. The tree grows to 35 metres (115 feet) tall, with an upright, symmetrical crown and horizontal branches. The fruit is corky and light and dispersed by water. As the tree gets older, its crown becomes more flattened to form a spreading, vase shape. Its branches are distinctively arranged in tiers. The leaves are large, 15–25 cm (6–9+3⁄4 in) long and 10–14 cm (4–5+1⁄2 in) broad, ovoid, glossy dark green, and leathery. They are dry-season deciduous; before falling, they turn pinkish-reddish or yellow-brown, due to pigments such as violaxanthin, lutein, and zeaxanthin.
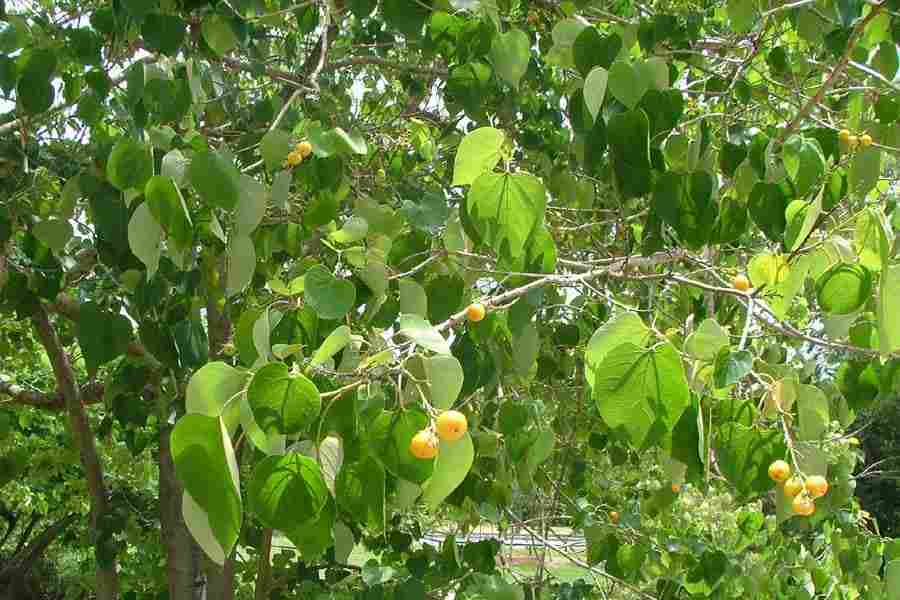

Gmelina arborea
Gmelina arborea, (in English beechwood, gmelina, goomar teak, Kashmir tree, Malay beechwood, white teak, yamane), locally known as gamhar, is a fast-growing deciduous tree in the family Lamiaceae. Gmelina arborea grows naturally throughout India, Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam and in southern provinces of China. It is found at altitudes from sea level to 1,500 metres (5,000 ft). Since the 1960s, it has been introduced extensively as fast-growing timber trees in Brazil, Gambia, Honduras, Ivory Coast, Malaysia, Malawi, Nigeria, the Philippines, and Sierra Leone. It is also planted in gardens and avenues. The Lion Throne, the most important, and last surviving, of the eight royal thrones of Myanmar, now in the National Museum in Yangon, is carved from Gmelina arborea wood.
Tecoma stans
Tecoma stans is a species of flowering perennial shrub in the trumpet vine family, Bignoniaceae, that is native to the Americas. Common names include yellow trumpetbush, yellow bells, yellow elder, ginger Thomas. Tecoma stans is the official flower of the United States Virgin Islands and the floral emblem of The Bahamas. Tecoma stans is a semi-evergreen shrub or small tree, growing up to 10 m (30 ft) tall. It features opposite odd-pinnate green leaves, with 3 to 13 serrate, 8- to 10-cm-long leaflets. The leaflets, glabrous on both sides, have a lanceolate blade 2–10 cm long and 1–4 cm wide, with a long acuminate apex and a wedge-shaped base. The large, showy, golden yellow, trumpet-shaped flowers are in clusters at the ends of branches. The corolla of the flower is bell- to funnel-shaped, five-lobed (weakly two-lipped), often reddish-veined in the throat and is 3.5 to 8.5 cm long. Flowering takes place from spring to fall, but more profusely from spring to summer.

Plumbago zeylanica
Plumbago zeylanica L. is a perennial herb with various pharmacological properties. It is used in Ayurveda, traditional medicine and cosmetics for its antimicrobial, hepatoprotective,anticancer, antifertility and wound healing.
Indigofera tinctoria
The popular color “indigo” is named after several plants in the genus Indigofera. These varieties of indigo are famous for the natural blue colors obtained from the plant leaves used to make a natural dye. Some indigo plant varieties are used medicinally, while others are beautiful and ornamental. Read on for more indigo plant information and an overview of the different indigo plants.
Gendarussa vulgaris
A small, erect, fast-growing, branched shrub with attractive, lanceolate (shaped like a lance-head), ascending to spreading variegated leaves in shades of green, white and grey, and produces dainty white flowers.
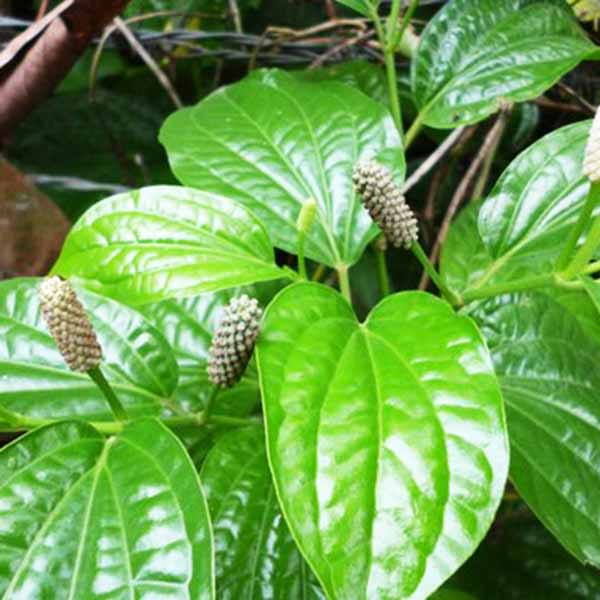

Piper longum
Long pepper is a slender aromatic climber and creeping jointed stems and fleshy fruits are embedded into the spikes. The Leaves are of dark green color. Flowers of this plant are monoecious. Male and female flowers are borne on different plants. Leaves are ovate or heart shaped having dark green color above and pale green below.
Bacopa monnieri
Bacopa monnieri is a medicinal creeping perennial in the Scrophulariaceae family with small oblong leaves and white to purple flowers frequently used in ayurvedic medicine. Other names for this herb include brahmi, water hyssop, thyme-leaved gratiola, and the herb of grace.

Carum carvi
Caraway is a plant with a long history that is native to western Asia, Europe and North Africa. It is said to have been used in cooking for centuries. Indeed, the caraway plant was mentioned by the ancient Greeks, and caraway seeds were used in recipes during Roman times. Caraway is known by many names, including karauya, Persian cumin, field cumin, meadow cumin, and meridian fennel. It is best known for its spicy and pungent caraway seeds; however, the caraway plant’s foliage and taproot can also be used in cooking.
Curcuma aromatica
Curcuma aromatica (common name: wild turmeric) is a member of the genus Curcuma belonging to the family Zingiberaceae.[2] Botanically close to Curcuma australasica, wild turmeric has been widely used as a cosmetic herbal in South Asia and nearby regions.Wild turmeric has rhizomes with a peculiar fragrance and cream color. The rhizomes are often used as a culinary ingredient, and in traditional medicine, for skin disorders and as an antibacterial agent. It is also commonly used in ethnic cosmetic products
Vitis quadrangularis
Historically, it has been used to treat many conditions, including hemorrhoids, gout, asthma, and allergies. However, recent research has found that this power-packed plant may also help promote bone health, relieve joint pain, and protect against chronic conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and stroke.

Zingiber wightianum
Description Zingiber wightianum (also called Wight's Ginger, among many other common names) is a species of plant in the Zingiberaceae family. It is a herbaceous perennial that can reach up to 1 m in height. It is native to the tropical regions of Southeast Asia. It is found in tropical rainforests, in the understory of the forest, and in secondary forests. Uses & Benefits Zingiber wightianum is used as a traditional medicine to treat digestive issues, fever, and headaches. It is also used as a flavoring agent in food. Flower, Seeds and Seedlings Zingiber wightianum has yellow flowers with 3 petals. Its seeds are small and black. The seedlings are small and have long, thin leaves.
Cocculus hirsutus
The juce of riped berries were used to make a durable bluish-purple ink. Stems and roots – used as in febrile conditions, dysentery, heart trouble and urinary disorders.
Tinospora cordifolia
Tinospora cordifolia commonly named as “Guduchi” is known for its immense application in the treatment of various diseases in the traditional ayurvedic literature.
Tinospora sinensis
Chinese Tinospora is a dietary supplement that is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) to help boost the immune system, reduce inflammation, and improve overall health. It is also used to treat a variety of conditions, including diabetes, cancer, and liver disease.
Cymbopogon citratus
Lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus), sometimes called lemon grass or citronella, is a tall grass-like ingredient commonly used in Southeast Asian cooking. The lower stalks and bulbs of the plant have a fresh, clean, lemony scent that is sometimes also added to non-alcoholic beverages, as well as teas, marinades, curries, and broths.
Pimenta dioica
Allspice — also known as Jamaican pepper, pimienta, or newspice — is a single spice with a unique flavor profile described as a blend of up to four different spices, hence the name. Since it’s a spice, it’s usually consumed in small amounts. However, allspice has also been used in folk medicine due to its potential health benefits
Clitoria ternatea
Butterfly pea flower is rich in antioxidants and linked to several health benefits, including weight loss, blood sugar control, and hair and skin health. Cosmetic manufacturers boast about butterfly pea flowers’ effectiveness in everything from skin care serums to hair mists and shampoos.

Adhatoda beddomei
Malabar Nut is valued for its therapeutic properties, especially in treating respiratory conditions like asthma, bronchitis, cough, and cold. It is known for its bronchodilator, expectorant, and anti-inflammatory effects.
Morus alba
White mulberry is a leafy tree with the scientific name of Morus alba.This tree is native to China, Japan, and India but is now a naturalized plant worldwide. White mulberry is considered an invasive species in the United States. That means it contributes to the destruction of established natural habitats. White mulberry contains bioactive compounds, which are also known as phytochemicals. White mulberry may work through these bioactive plant chemicals. So, white mulberry might have different properties and activities depending on the specific plant chemical.

Coleus aromaticus
Coleus aromaticus has been used in herbal medicines or folk medicine to treatment conditions such as cold, asthma, constipation, headache, cough, fever and skin diseases. The leaves of the plant are used as flavoring agents, or incorporated as ingredients in the preparation of conventional food.

Syzygium cumini
In traditional medicine systems like Ayurveda, various parts of the Java plum tree, including the fruit, seeds, bark, and leaves, are used for their medicinal properties. The fruit is believed to have diuretic, astringent, and anti-diabetic properties. It is often used in the treatment of diabetes, digestive disorders, and urinary problems.
Coleus vettiveroides
It is widely used in folk medicine to treat conditions like cold, asthma, constipation, headache, cough, fever and skin diseases. The leaves of the plant are often eaten raw or used as flavoring agents, or incorporated as ingredients in the preparation of traditional food.

Asparagus racemosus
Health benefits of Shatavari include improvement in reproduction and anti-anxiety effects. Possible side effects include allergic reactions. hatavari is a species of asparagus plant that has been used for many centuries in Indian Ayurvedic medicine. Shatavari, also known as satavari, satavar, or Asparagus racemosus (A. racemosus), is said to promote fertility and have a range of health benefits, particularly for the female reproductive system. The herb is thought to be adaptogenic, which means that it may help to regulate the body’s systems and improve resistance to stress.

Kaempferia rotunda
It is an important Indian medicinal herb that has a long history of use in the treatment of several kinds of human ailments including vata ailments like cough and cold, fever, headache, pains disorders, skin diseases, rheumatic diseases, arthritis, joint fractures, vertigo, wounds, gastritis, antidote for snake venoms, inflammation, blood vomiting, mouth sores and tongue blisters in infants.

Vanilla planifolia
Today, Bourbon vanilla is highly prized for its smooth, creamy, and sweet flavor, making it a popular ingredient in various culinary creations, including desserts, baked goods, and beverages. It is also widely used in perfumery and aromatherapy due to its intoxicating scent.

Aloe barbadensis miller
Aloe vera has a long history of medicinal use, dating back thousands of years to ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans. It was prized for its healing properties and was often referred to as the "plant of immortality" by the Egyptians.
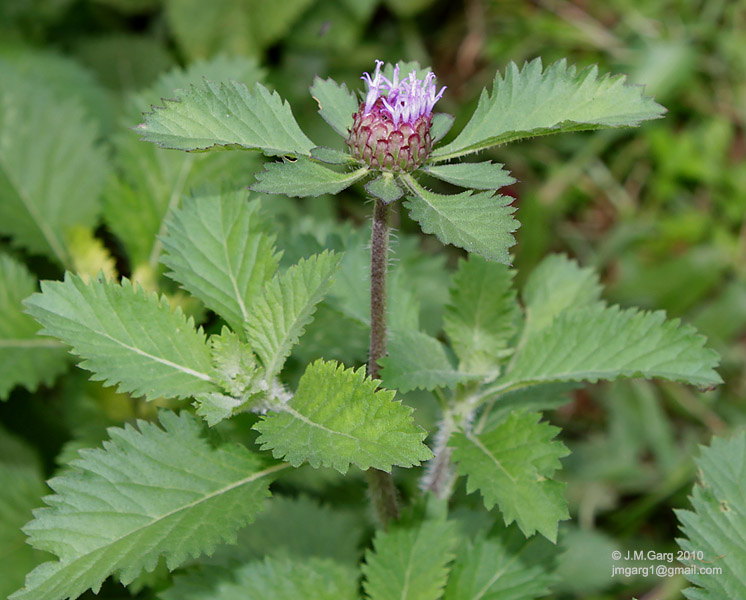

Centratherum punctatum
C. punctatum has been primarily used as an ornamental. However, recently it has been used in studies which have shown that leaf extracts exhibit antimicrobial, antioxidant and anti-proliferative properties and suggest that this species might be used a potential medicinal agent. Similarly in Nigeria, a research group has shown that essential oils extracted from C. punctatum may also have antimicrobial properties
Ficus krishnae
Indian Ficus species possess anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, antidiabetic, antiarthritic, antistress, anticancer, hepatoprotective, neuroprotective and wound healing properties. The phytochemical analysis reveals the presence of alkaloids, triterpenoids, flavonoids, furanocoumarins, and polyphenolic compounds. Ficus krishnae is a perennial plant, used in number of folklore medicine, to treat ulcer, vomiting, fever, inflammation, diabetes, dysentery, leprosy and cancer etc.

Elaeocarpus sphaericus
It is used in folk medicine in treatment of stress, anxiety, depression, palpitation, nerve pain, epilepsy, migraine, lack of concentration, asthma, hypertension, arthritis and liver diseases.

Piper nigrum
Black pepper, scientifically known as Piper nigrum, is one of the most commonly used spices worldwide. Here's an interesting fact about black pepper:
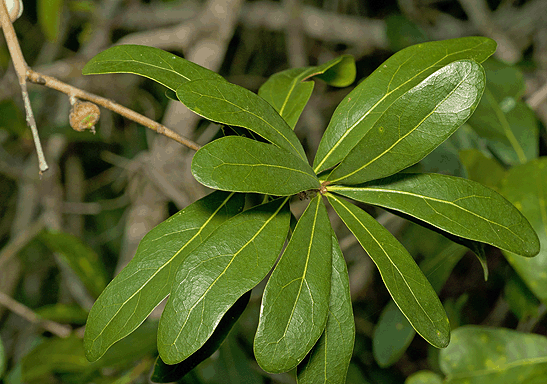
Hydnocarpus laurifolia
Medicinal uses: Skin diseases, scrofula, rheumatism, eczema, leprosy, sprains, wounds and sores, Intestinal worms, helminthiasis, and infected wounds. The chemical contents: Antineoplastic, anti-inflammatory, hypnocarpic acid, chaulmoorgic acid.
Lagerstroemia speciosa
Blood Sugar Regulation: One of the prominent health benefits of Lagerstroemia speciosa is its potential to regulate blood sugar levels. Compounds like corosolic acid may play a role in improving insulin sensitivity.
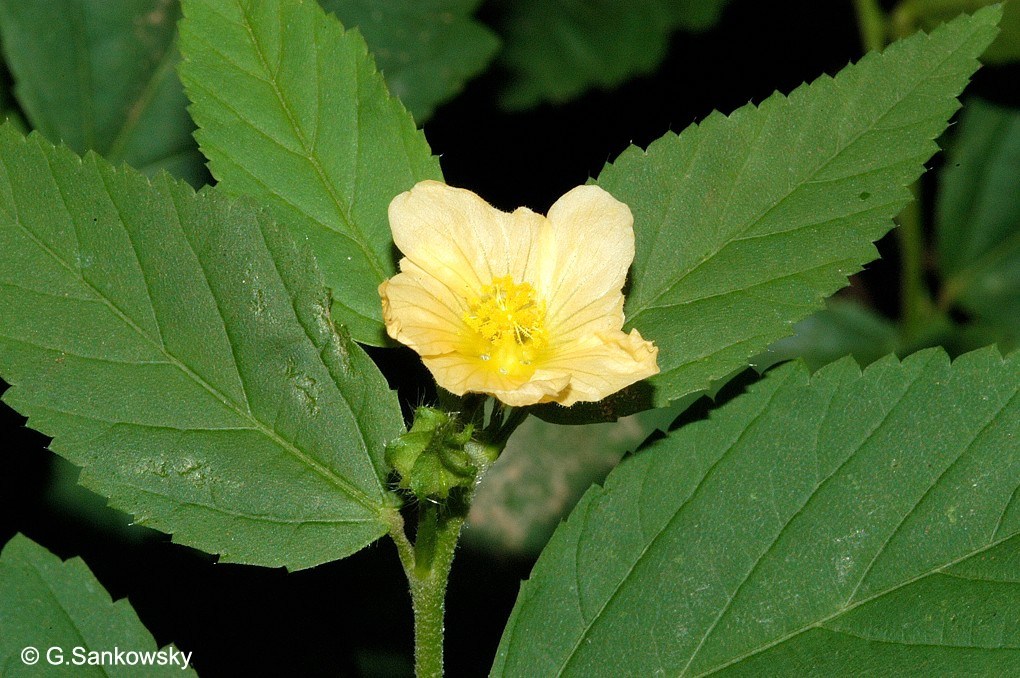

Sida rhombifolia
Arrowleaf sida has a long history of use in traditional medicine systems, particularly in South America and the Caribbean. Various parts of the plant, including the leaves, roots, and seeds, are used to prepare herbal remedies for a range of ailments. It is believed to have diuretic, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic properties and has been used to treat conditions such as urinary tract infections, digestive disorders, and skin ailments.
Ocimum kilimandscharicum
Ocimum kilimandscharicum is one of a few types of basil that is perennial. It is a well known plant in Indian traditional system of medicine. Ocimum kilimandscharicum plant is widely used in the management of various ailments including colds, coughs, abdominal pains, measles, anti-ulcer, bronchitis, anorexia, memory disorders and diarrhoea.

Annona muricata
Soursop (also called graviola, guyabano, and in Latin America guanábana) is the fruit of Annona muricata, a broadleaf, flowering, evergreen tree. It is native to the tropical regions of the Americas and the Caribbean and is widely propagated.[6] It is in the same genus, Annona, as cherimoya and is in the Annonaceae family. The soursop is adapted to areas of high humidity and relatively warm winters; temperatures below 5 °C (41 °F) will cause damage to leaves and small branches, and temperatures below 3 °C (37 °F) can be fatal. The fruit becomes dry and is no longer good for concentrate. With an aroma similar to pineapple, the flavor of the fruit has been described as a combination of strawberries and apple with sour citrus flavor notes, contrasting with an underlying thick creamy texture reminiscent of banana.

Ocimum tenuiflorum
Holy basil (Ocimum tenuiflorum) is native to Southeast Asia. It has a history within Indian medicine as a treatment for many conditions, from eye diseases to ringworms. This green leafy plant, also known as Ocimum sanctum L. and tulsi, is considered a tonic for the body, mind, and spirit. Different parts of the plant are recommended for treating different conditions: Use its fresh flowers for bronchitis. Use the leaves and seeds, with black pepper, for malaria. Use the whole plant for diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Use the pill and ointment form for eczema. Use an alcohol extract for stomach ulcers and eye diseases. Use an essential oil made from the leaves for insect bites.
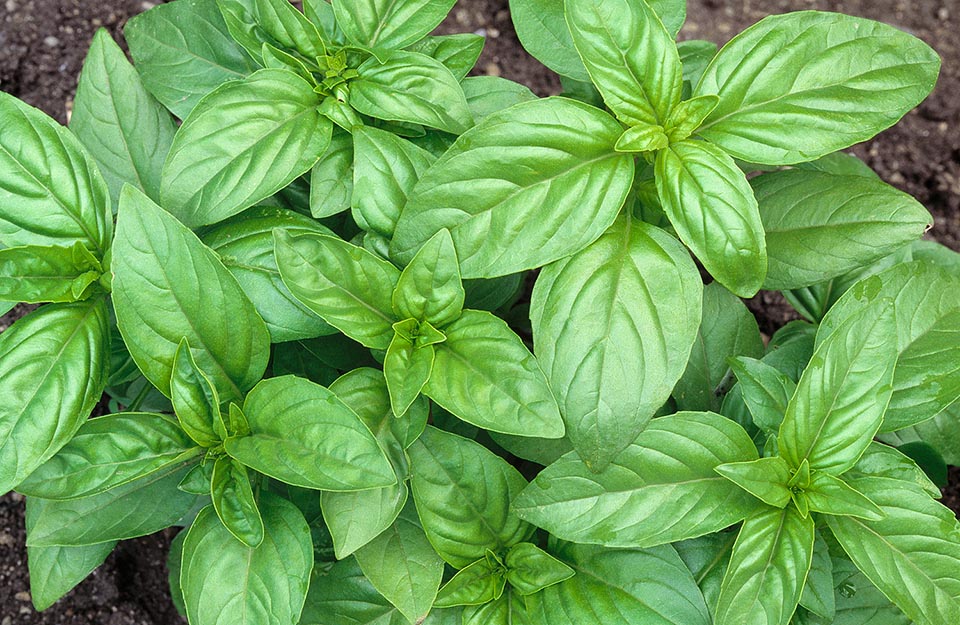

Ocimum basilicum
The plant extracts have excellent potential to be used as medicinal raw materials, and exhibit an extensive variety of therapeutic capacities, including antibacterial, antioxidant, wound healing, anti-inflammatory, antifungal, and antiviral properties. Keywords: Ocimum basilicum, antimicrobial, antiviral, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory

Eucalyptus tulsi
Different parts of the plant are recommended for treating different conditions: Use its fresh flowers for bronchitis. Use the leaves and seeds, with black pepper, for malaria. Use the whole plant for diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Use the pill and ointment form for eczema. Use an alcohol extract for stomach ulcers and eye diseases.
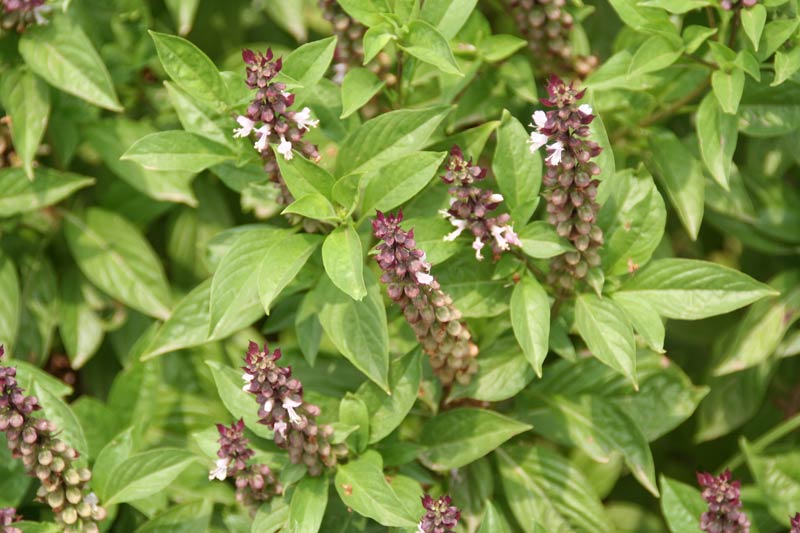

Ocimum sanctum
The fragrant leaves and flowers, in the form of tincture, tea or decoction are considered to be stomachic and expectorant, used in treating coughs, bronchitis, skin diseases, and diarrhea. These preparations are considered to be prophylactic against epidemics including cholera, influenza and malaria.

Sphenodesme paniculata
In botanical terminology, "panicled" typically refers to a type of inflorescence, where flowers are arranged in a branching, pyramidal shape. "Varshiki" sounds like it could be a specific variety, species, or perhaps a regional term, but without further context or information, it's challenging to provide a specific definition or explanation.
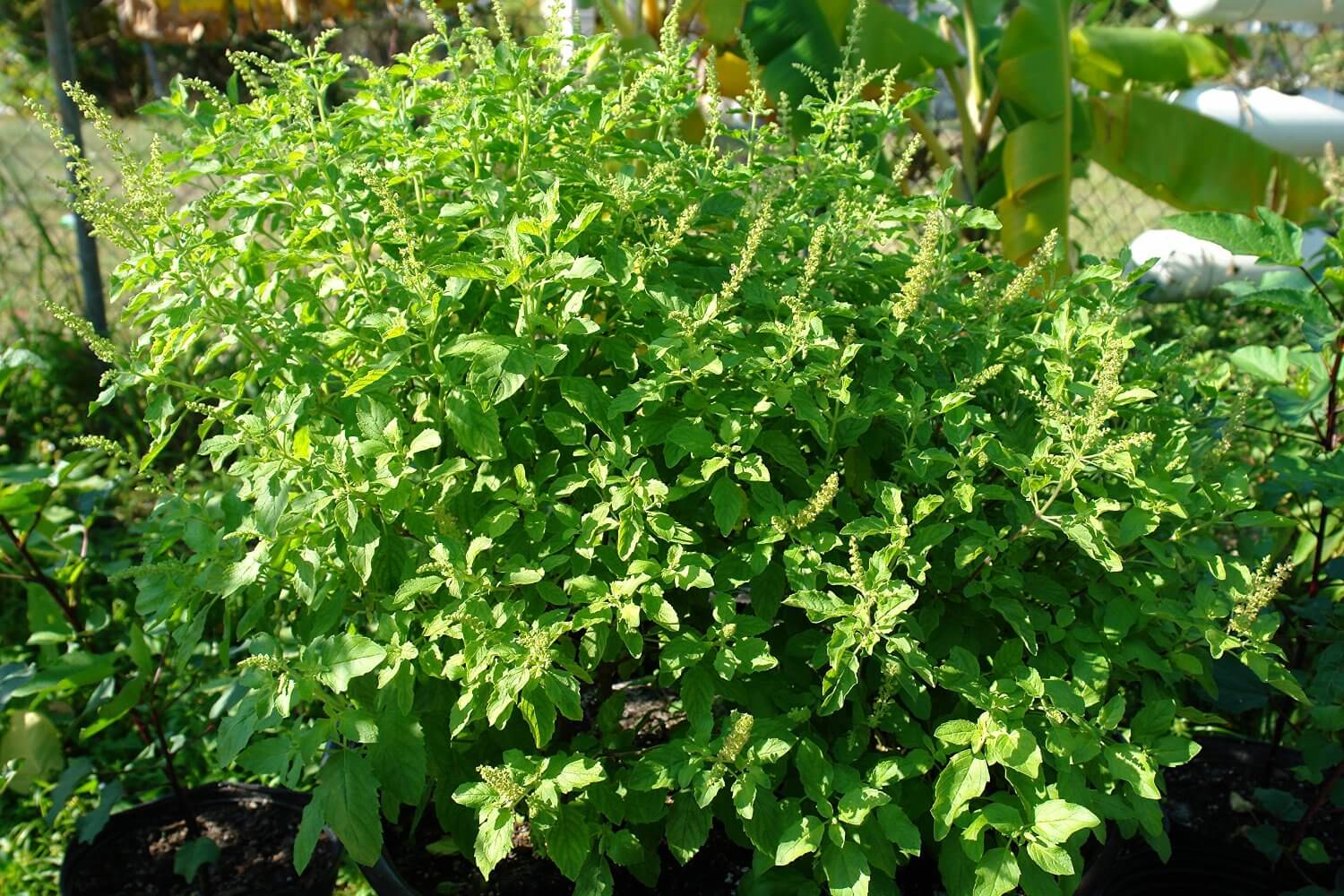

Ocimum tenuiflorum
Apart from these common ailments, Ayurveda also recognizes its use for the diseases ranging up to tumerous growths. Experimental studies identify it to be a highly promising immunomodulator, cytoprotective and anticancer agent. Following are the benefits & uses of Tulsi plant or Holy Basil/Ocimum Sanctum. This green leafy plant, also known as Ocimum sanctum L. and tulsi, is considered a tonic for the body, mind, and spirit. Different parts of the plant are recommended for treating different conditions: Use its fresh flowers for bronchitis. Use the leaves and seeds, with black pepper, for malaria. Use the whole plant for diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Use the pill and ointment form for eczema. Use an alcohol extract for stomach ulcers and eye diseases. Use an essential oil made from the leaves for insect bites.
Coleus aromaticus
Coleus aromaticus has been used in herbal medicines or folk medicine to treatment conditions such as cold, asthma, constipation, headache, cough, fever and skin diseases. The leaves of the plant are used as flavoring agents, or incorporated as ingredients in the preparation of conventional food.
Madhuca indica
Native to North America, the black locust produces fragrant white flowers that are highly attractive to bees. The resulting honey is light in color and has a delicate flavor.
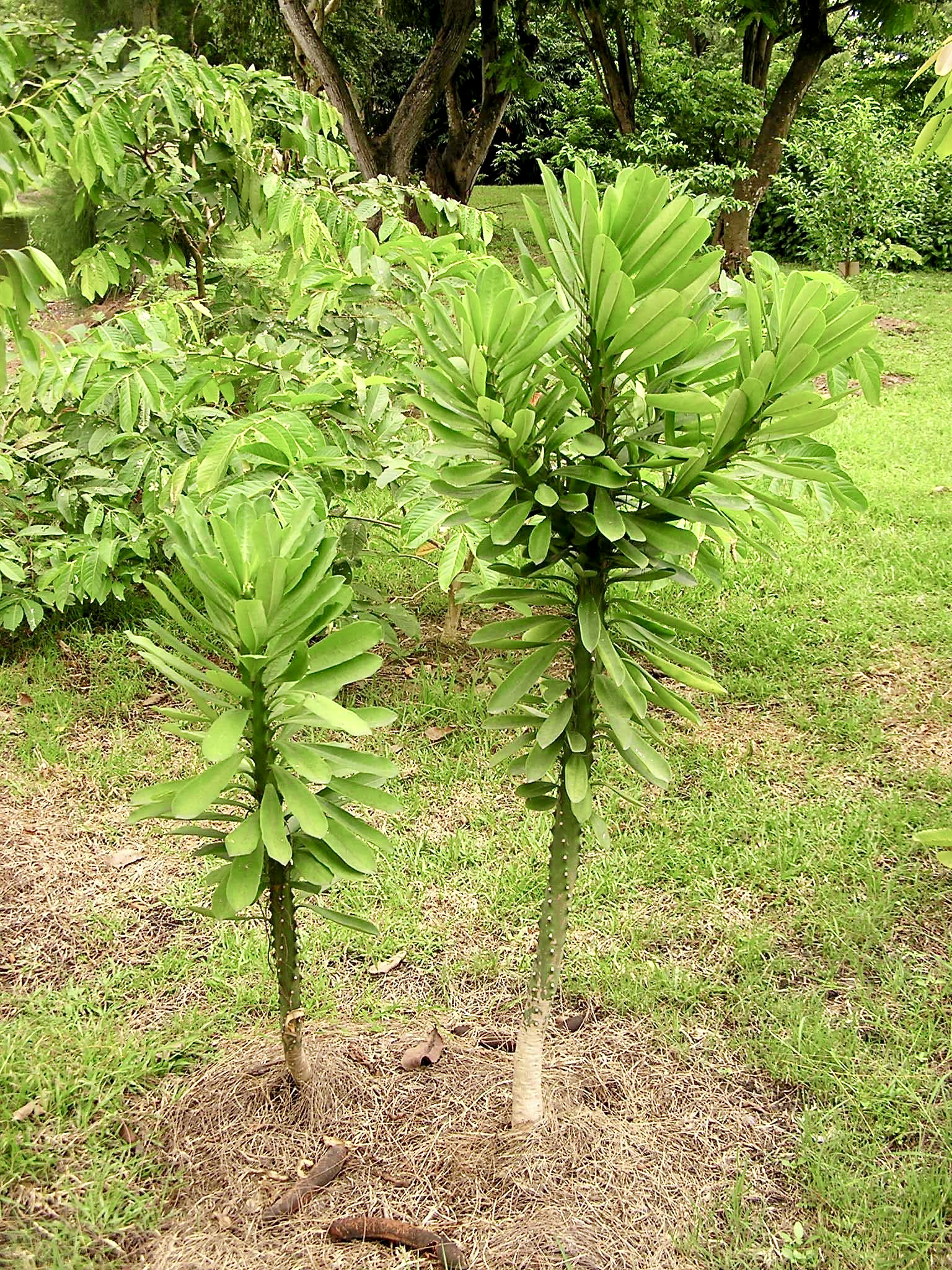

Euphorbia nivulia
Euphorbia nivulia typically grows as a succulent shrub or small tree. It has a thick, fleshy trunk and branches, which are armed with spines. The plant can grow up to 3-5 meters in height.
Ficus microcarpa
The Chinese banyan produces small, round figs that turn from green to purple as they ripen. These figs are an important food source for birds and other wildlife.
Alternanthera sessilis
Alternanthera Sessilis will help to reduce the conditions of the following disease like body heat, eye irritation, knee pain, white discharge, helps to recover from the loss of appetite, liver diseases. The extract and oil from sessilis help to reduce the body heat during the summer season and helps to prevent headaches.
Vitex negundo
he plant is said to have a variety of therapeutic uses due to its abundance of phytochemicals, including antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, astringent, bronchodilator, CNS depressant, emmenagogue detoxifying, diuretic, anticancer, and hepatoprotective properties. In addition, it has larvicidal, insecticidal, and repellent uses. Vitex negundo or nirgundi is an herb widely used in Ayurvedic, Chinese and western herbalism traditions. Let’s take a look at nirgundi’s Ayurvedic properties, uses, and benefits. It is a shrub or small tree native to the tropical regions of Asia as well as Eastern and Southern Africa, commonly found growing near bodies of water. Vitex Nergundo or Nirgundi can be used in various forms like juice, powder, capsules, and oil. Vitex Nergundo juice, powder, and capsules can be taken with warm water once or twice a day. Whereas, oil extracted from Vitex Nergundo can be applied externally on the affected areas.

Magnolia champaca
Champa is a large evergreen tree widely distributed in Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Burma, India, China, Bangladesh, Thailand and Malaysia. M. champaca L. has traditionally been used to treat diarrhea, cough, bronchitis, hypertension, dyspepsia, fever, rheumatism, abscesses, dysmenorrhea and inflammation.
Indigofera tinctoria
Medicinal uses: True Indigo used for Glowing Skin, Sores, Ringworm, Blisters, Hair rejuvenation, natural hair darkening, removing Worms in Teeth and Gums, Sores on Skin, Liver, Urinary problems and poison, Mouth ulcers or Canker sores, Kidney disease, Insects in Ear, Black Hair and Hair fall, Dog bite.
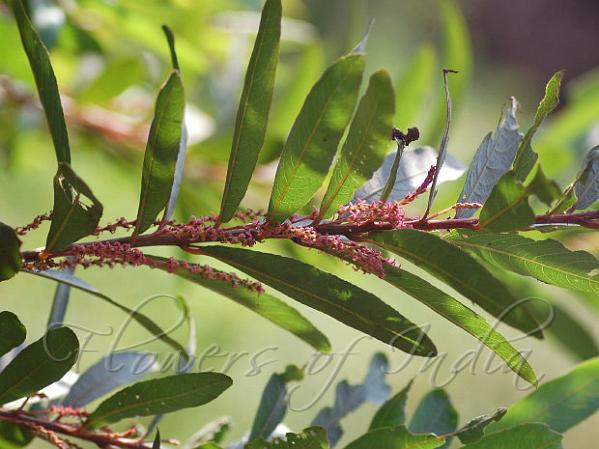

Homonoia riparia
illow-Leaved Water Croton is a plant commonly found growing along small streams at low and medium altitudes, on banks, and in streambeds. It is a shrub growing to 1-3 m tall. The leaves are linear-lanceshaped, 12-20 cm long, and 1.5-2 cm wide. Upper surface of the leaves is green and shining, and the lower surface brown and hairy. Reddish flowers are born in spikes 5-10 cm long, with obovate bracts, 1.5-2 mm long. Male flowers have 0.2 mm long stalks, 3 velvety sepals, 3-4 mm long. Female flowers have 5 oblong sepals, with tapering tips, about 1-2 mm long. The capsules are about 8 mm in diameter, hairy, and borne on solitary, hairy spikes, 5-12 cm long, in leaf axils. Medicinal uses: Warning: Unverified information A decoction of the root is a laxative and diuretic and is used in piles, stone in the bladder, gonorrhea, syphilis and thirst.
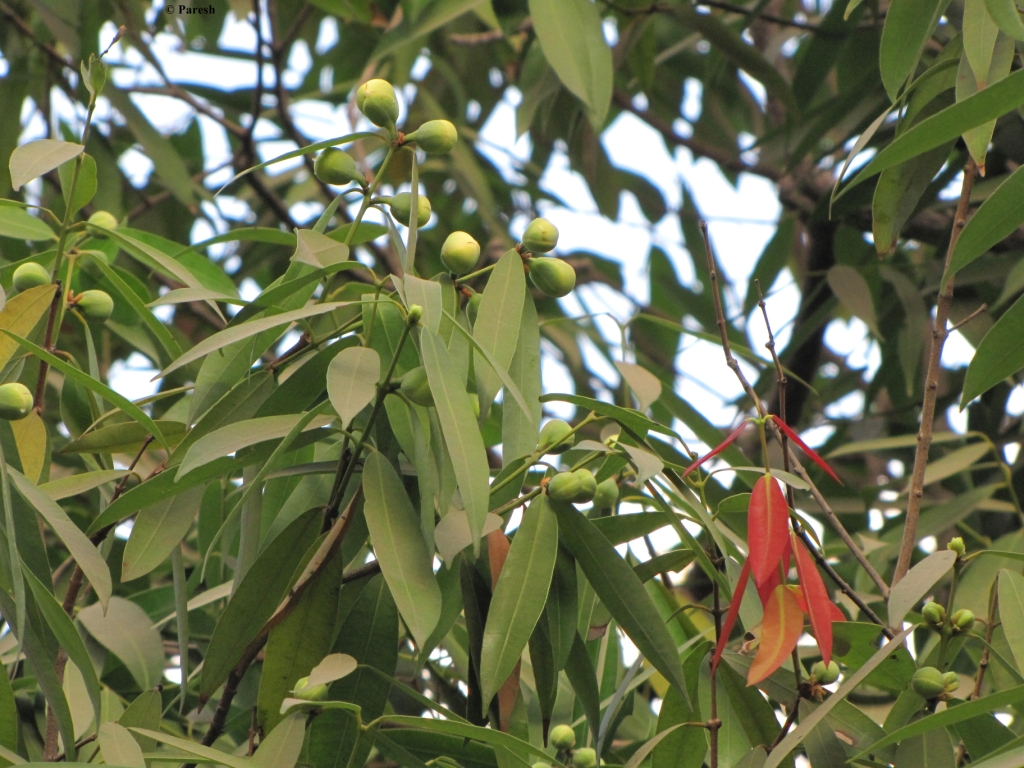

Mesua ferrea
t is also known as Cobra Saffron, Ceylon Ironwood, Indian rose chestnut and Sirunagappu in Ayurveda. It balances the three Doshas of the body. It is considered mainly in bleeding disorders that occur due to the Pitta (heat) imbalance. Nagkesar flowers have many traditional medicinal uses. The dried flowers are used in case of bleeding piles, dysentery with mucus, irritability of the stomach, excessive perspiration, skin infections, cough and indigestion. Nagkesar flowers are also used as an astringent and for snake bite and scorpion stings.
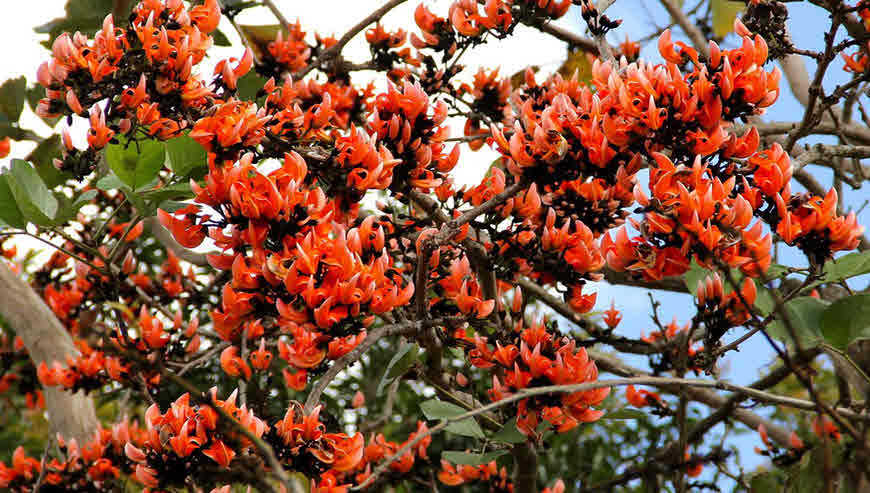

Butea monosperma
In India, the seeds are used for skin ailments; keratitis; piles; urinary discharges; and diseases of the brain, eye, head, and skin. The juice from the plant as well as the oil is antiseptic. It is an excellent remedy for itch and herpes. The seeds are hematinic, bitter, and acrid. They are known to have astringent, diuretic, and tonic properties. Palash stem bark might be used in traditional medicine system to treat dyspepsia, diarrhoea, ulcers, sore throat, and snakebite. Palash wood pulp may be used to treat liver problems, gonorrhoea, wound infections, night blindness and snakebite treatment.

Cassia fistula
C. fistula has been used for a long time both orally and topically for healing of wounds and burns in traditional medicine by the tribal communities of several countries. maltas helps in increasing the immunity of the body. Amaltas pulp is used to cure mouth ulcers. It is a very beneficial medicine for healing wounds. Taking decoction(Kadha) of its root provides relief in fever. It is a very useful herb for skin-related diseases.
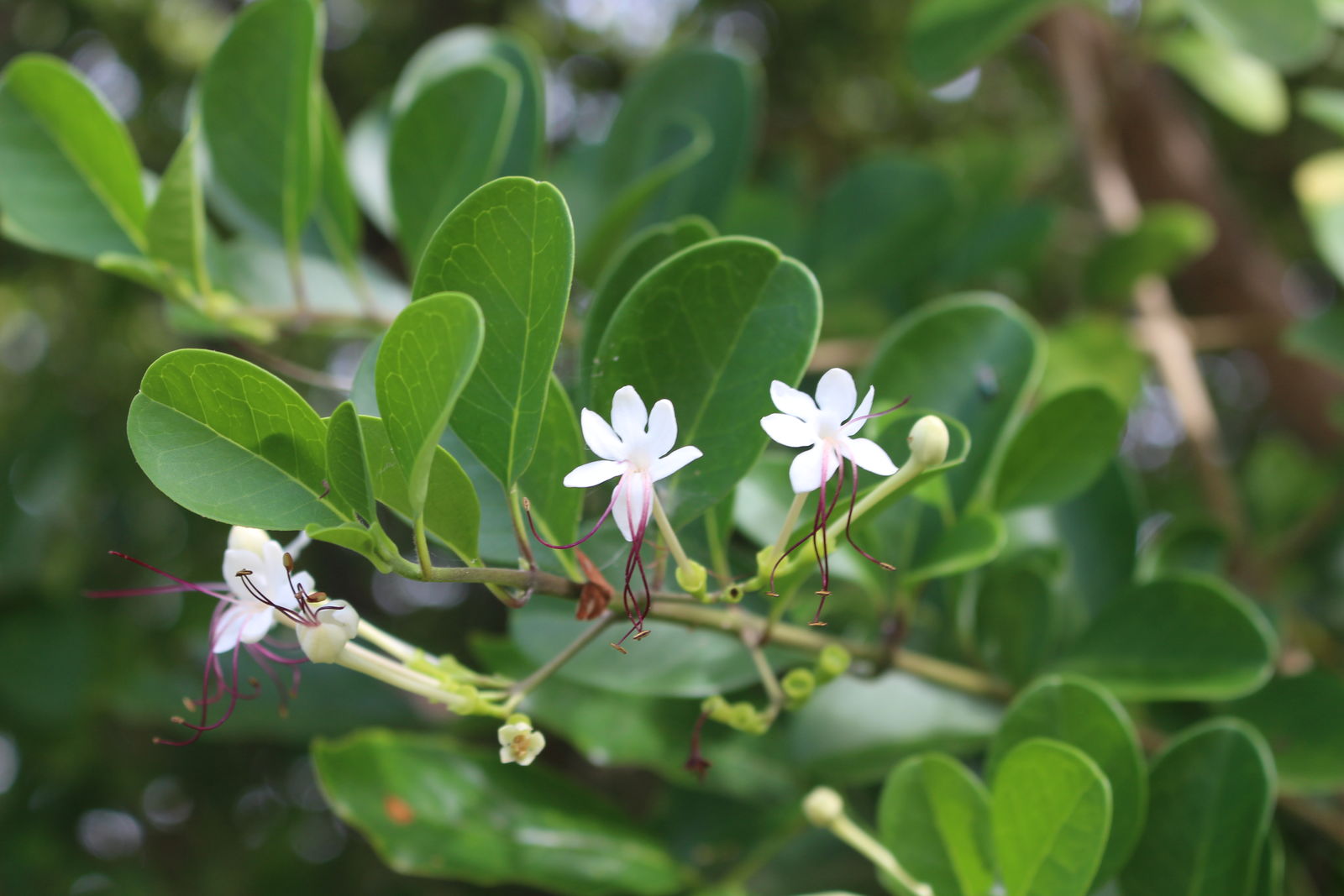

Volkameria inermis
A decoction of the root is administered as a febrifuge and general alterative. The leaves are used in poultices as a resolvent. Its seeds or its finely ground roots are used as a remedy for an upset stomach, especially if caused by poisonous seafood. Pharmacological studies have shown that these compounds and extracts from the Clerodendrum genus have extensive activities, such as anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive, anti-oxidant, anti-hypertensive, anticancer, antimicrobial, anti-diarrheal, hepatoprotective, hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic.

Neolamarckia cadamba
Neolamarckia cadamba, also known as "kadam", is an evergreen tropical tree in the Rubiaceae family that has been used in Ayurvedic medicine for centuries to treat many ailments. The plant's various parts, including the bark, leaves, flowers, and roots, have been used to treat a range of conditions, including. Cadamba are used in the treatment of various ailments such as fever, uterine complaints, blood diseases, skin diseases, tumour, anaemia, eye inflammation and diarrhoea. Other reported uses of N. cadamba include antihepatotoxic, antimalarial, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, diuretic and laxative

Bauhinia phoenicea
Bauhinia phoenicea, also known as Vallimantharam, is a medicinal climbing shrub endemic to the Western Ghats. In traditional medicine, it's used to treat a variety of ailments, including: diabetes, skin allergies, fungal infections, worm disturbances, and wounds. his plant is used traditionally in dropsy, pain, rheumatism, convulsions, delirium, and septicemia. [1] The bark of the plant is used as an astringent in the treatment of diarrhea. Its decoctions are recommended for ulcers as a useful wash solution.
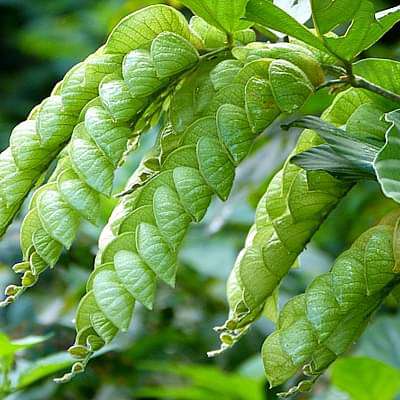

Phyllodium longipes
Genus epithet 'Phyllodium' describes a flattened leaf-like stem, a reference to the leafy bracts enclosing the plant's flowers. Species epithet 'longipes' means 'long-stalked', alluding to the trailing inforescence shoots. Others: Root decoction used to treat kidney stones, bodily discomfort and cancer. P. pulchellum is reported to be used as fodder and as an edible plant. The plant is used as insect repellent and is used for treating cancer, hemorrhages, fever, edema, liver injury and viral infections.

Phaleria macrocarpa
Phaleria macrocarpa (Scheff.) Boerl., also known as Mahkota Dewa, is a plant native to Papua Island, Indonesia that has been used in traditional medicine for a variety of purposes. The leaves, stems, fruit, and seeds of the plant have all been used to treat different ailments. Phaleria macrocarpa (Scheff.) Boerl. is geographically distributed around Papua Island, Indonesia. Traditionally, P. macrocarpa is exercised to reduce pain, stomachache, diarrhea, tumor problems, blood glucose, cholesterol, and blood pressure.

Morinda citrifolia
Morinda citrifolia, commonly known as the noni berry, is used to prepare the health drink called NONI juice. It is used in Polynesian herbal remedies to treat diseases such as cancer, gastric ulcers, depression, etc. Historically, noni has been used for thousands of years in Polynesia as a food source and for medicinal uses (usually applied to the skin). Today, noni is promoted as a dietary supplement to prevent cancer, prevent infections, treat high blood pressure, and help with other conditions.

Annona muricata
A. muricata leaves are used to treat headaches, insomnia, cystitis, and cancer, the seeds are used to treat parasitic infections, and the fruit is used to treat diarrhea and neuralgia, eliminate worms and parasites, increase milk production in lactating women, and reduce fever. he dried leaves of Annona muricata are used orally for analgesic effects in some parts of Indonesia. In Burkina-Faso, the bark and roots of Annona muricata are used for dysentery and as an anthelmintic medicine, whereas the leaves are utilized for both fever and dysentery.

Bauhinia acuminate
The roots are used by the Javanese to treat cough and cold. In India, the decoction of leaves and bark is used. to treat asthma attack.

Simarouba glauca
People take simaruba for diarrhea, dysentery, malaria, water retention (edema), fever, and stomach upset. It is also used as a tonic. Women use it to cause abortion. The wood is generally insect resistant and is used in the preparation of quality furniture, toys, matches, and as pulp (in paper making). It also can be used for industrial purposes in the manufacture of biofuel, soaps, detergents, lubricants, varnishes, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.

Boswellia glabra
Boswellia, also known as olibanum, is an herb used in Ayurvedic and Unani medicine to treat a variety of conditions. It's also used in cosmetics and perfumes. Boswellia is part of the Burseraceae family, which is known for its aromatic essential oils and resins. oswellia, also known as Indian frankincense, is an herbal extract from the Boswellia serrata tree. It may help reduce inflammation and benefit people with certain health conditions. Resin made from boswellia extract has been used for centuries in Asian and African folk medicine.

Pterocarpus santalinus
The heartwood of red sanders is used as an astringent and tonic, and is bitter, sweet, cooling, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and febrifuge. Its decoction is given in chronic dysentery. In Ayurveda, an Indian system of traditional medicine, it is mentioned that the heartwood of the plant is used as external application for treating inflammation, diabetes, headache, skin diseases, and jaundice, and in wound-healing.

Bougainvillea glabra
In Mandsaur, India, bougainvillea helps reduce heartburn, treat sore throat, leucorrhea, blood vessels and hepatitis. To improve intestinal disorders extracts of B. glabra are used in Africa. It also is believed to have anticancer, antihepatotoxic, anti-inflammatory, antihyperlipidemic, antimicrobial, antioxidant, and antiulcer properties. Bougainvillea spectabilis contains pinitol, which has an insulin-like effect and has the potential for development as a treatment for diabetes.

Mimusops elengi
"Spanish cherry" likely refers to the Spanish variety of cherry, known for its sweetness and juiciness. Spain produces several varieties of cherries, including the popular Bing and Rainier types. These cherries are often enjoyed fresh or used in various culinary dishes and desserts.

Diospyros ebenum
Ceylon ebony, scientifically known as Diospyros ebenum, is a species of tree native to Sri Lanka (formerly known as Ceylon), as well as southern India and Indonesia. It is renowned for its dark, dense wood, which has been highly prized for centuries due to its beautiful black color and fine grain. Ceylon ebony has historically been used in the crafting of high-end furniture, musical instruments (such as pianos, guitars, and violins), decorative objects, and luxury items like chess pieces and walking sticks.

Saraca asoca
Various parts of the Ashoka tree, including its bark, leaves, flowers, and seeds, have been used in traditional Ayurvedic medicine for centuries. It is believed to have therapeutic properties and is used to treat a range of ailments, including gynecological issues, digestive disorders, and skin conditions.

Sapindus laurifolius
The leaves and fruits of the Sapindus laurifolius tree, also known as soapnut or reetha, have been used in traditional medicine to treat joint pain and yolk gall in cattle. The plant's powder is also used in cosmetics and contraceptive creams because of its antimicrobial properties. Plants of the genus Sapindus have been used in traditional medicine for the treatment of ulcers, external wounds, inflammation, epilepsy, dental caries, arthritis, joint pain, gout and rheumatism. Phytochemical studies of this genus have identified more than 103 compounds.

Boswelliaserrata
Indian olibanum has been used for centuries in traditional Indian Ayurvedic medicine for its various therapeutic properties. The resin is believed to possess anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antiarthritic properties, making it valuable in the treatment of conditions such as arthritis, rheumatism, and inflammatory bowel diseases. In Ayurveda, it is often administered internally or used externally in the form of incense, oils, or topical preparations to alleviate pain and inflammation and promote overall well-being. Its medicinal use continues to be studied for its potential health benefits in modern medicine.

Alstonia venenata
commonly known as devil's tree, is an important medicinal plant in the various folk and traditional systems of medicine in Asia, Australia, and Africa. The decoction, mostly prepared from the bark, is used to treat a variety of diseases of which the most important is malaria.. Roots and fruits are believed to be useful for skin diseases, leprosy, cobra and other venomous bites, epilepsy, fatigue, fever, syphilis, insanity, helminthiasis, epilepsy, as remedy for impure blood.

Gmelina arborea
The whole Gmelina arborea plant, also known as Gambhari, is used in Ayurvedic medicine for a variety of purposes. The plant is astringent, bitter, digestive, cardiotonic, diuretic, laxative, and a pulmonary and nervine tonic. It can help with: Digestion: The roots promote digestive power and improve memory. Fever: The roots and bark can help with fever. Heart disease: The roots can help with heart disease. Nervous disorders: The roots can help with nervous disorders. Piles: The roots can help with piles. Burning sensation: The roots can help with burning sensation. Hallucinations: The roots can help with hallucinations. Joint pain: The leaves can reduce joint pain and improve joint function in people with arthritis.

Pandanus amaryllifolius
Screw pines are distinctive for their aerial prop roots, which grow from the branches down towards the soil. These roots resemble screws or propellers, hence the name "screw pine." Unlike typical roots, these structures serve multiple purposes. They provide stability to the plant in the often windy coastal habitats where screw pines thrive. Additionally, they aid in water absorption, especially in environments with sandy or nutrient-poor soils, by capturing moisture from the air or collecting rainwater. The aerial roots also play a role in reproduction, as they can take root when they touch the ground, allowing the plant to propagate vegetatively.

Tabernaemontana divaricata
Tabernaemontana divaricata, also known as crepe jasmine, has many traditional medicinal uses, including: Anti-inflammatory, Anti-parasitic, Anti-microbial, Anti-tumor, Analgesic, Antioxidant, Brain tonic, Anti-epileptic, and Anti-mania. Tabernaemontana divaricata (Crepe jasmine) from the Apocynaceae family has been used in traditional medicines, frequently for fever, pain, and dysentery.

Homalocladium platycladum
Tapeworms are known for their remarkable longevity. Some species of tapeworms can live for years within their host's intestines, continuously growing and reproducing. For example, the adult stage of the Taenia solium tapeworm, which infects pigs and can also infect humans, can survive in the intestines for several years if left untreated. This longevity allows tapeworms to persistently draw nutrients from their host and produce thousands of eggs, contributing to their success as parasitic organisms.

Couroupita surinamensis
Extracts from tree's tissues have antiseptic and antifungal properties, used by Amazonian Shamans to treat malaria. Young leaves used medicinally to relieve toothache, leaf juice used to treat skin diseases, fruit pulp used to disinfect wounds. Parts of the plant have been used in traditional medicine. It has been used to treat hypertension, tumors, pain, and inflammation, the common cold, stomachache, skin conditions and wounds, malaria, and toothache, although data on its efficacy are lacking.

Samadera indica
Samadera indica (also known as Quassia indica or Nibam) is a plant that has been used in traditional medicine for many purposes. The different parts of the plant have different uses, including: Bark: Used to treat fevers, and as a stomachic, emmenagogue, and febrifuge tonic Seeds: Used to treat rheumatism, and as a liniment for bruises Leaves: Used to treat skin eruptions Fruit: Used to treat rheumatism
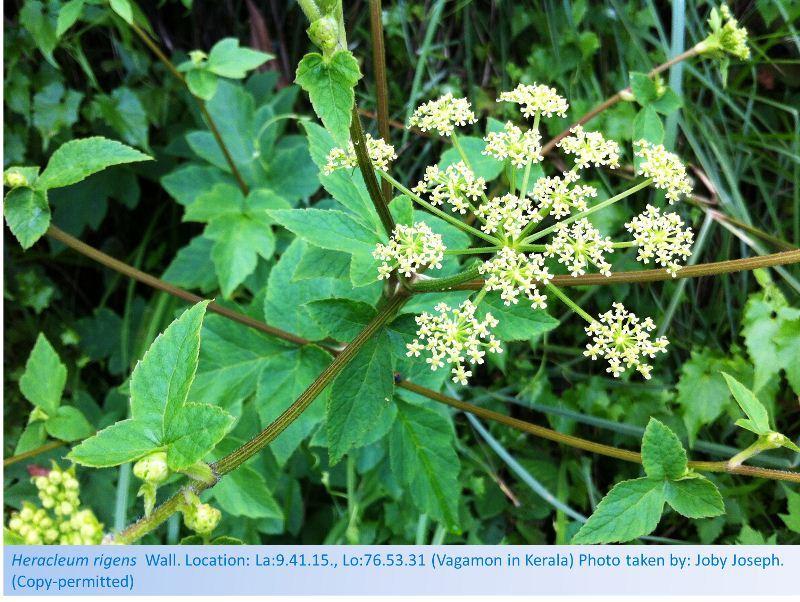

Heracleum rigens
Heracleum rigens, commonly known as Siberian hogweed or Russian cow parsnip, is a perennial herbaceous plant native to Asia, particularly found in regions like Siberia, China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan. It belongs to the Apiaceae family, which includes plants like carrots, celery, and parsley.

Coscinium fenestratum
False calumba has been traditionally used in African and Ayurvedic medicine for its medicinal properties. The roots of the plant contain compounds with potential therapeutic benefits, including as a digestive aid, to treat fever, and as an anti-inflammatory agent. In traditional medicine practices, false calumba has been used to alleviate gastrointestinal issues such as indigestion, diarrhea, and dysentery. However, it's essential to note that while traditional uses exist, scientific research on the efficacy and safety of false calumba is ongoing.

Gardenia jasminoides
Gardenia jasminoides, or gardenia, is a flowering plant native to southern China whose fruit has been used in traditional Asian medicine for centuries. Its flowers are also known for their fragrance in East Asia. The fruit of gardenia, Gardenia jasminoides Ellis, is a traditional Chinese folk medicine used in the treatment of an array of illnesses including jaundice, headaches, fever, inflammation, hepatic disorders, and hypertension.

Vateria indica
The Indian copal tree produces a resin known as dammar or copal resin. This resin has been used for various purposes throughout history, including as incense, varnish, and in traditional medicine. Dammar resin has a pleasant aroma when burned, making it popular in incense blends. It has also been utilized as a natural varnish in painting and woodworking, as well as in traditional medicine for its purported medicinal properties. The resin is harvested by making incisions in the tree's trunk, allowing the sap to flow and then harden into resin. This sustainable harvesting practice has been carried out for generations in regions where the Indian copal tree is native.

Gendarussa vulgaris
If you're referring to whether the Indian copal tree produces herbs or spices, it's important to note that it produces resin rather than herbs or spices commonly used in cooking. Resin from the Indian copal tree is primarily used for purposes such as incense, varnish, and traditional medicine, rather than as a culinary herb or spice.

Peltophorum pterocarpum
The Yellow Flame Tree, also known as Peltophorum pterocarpum, is a stunning flowering tree native to tropical regions such as Southeast Asia and Australia. It belongs to the legume family (Fabaceae). One of its most striking features is its vibrant yellow flowers, which resemble flickering flames, hence the name. The tree can reach heights of up to 60 feet (18 meters) and has a spreading canopy that provides ample shade. It's commonly planted for ornamental purposes in parks, gardens, and along streets due to its beautiful flowers and attractive foliage. The Yellow Flame Tree is also valued for its timber and in traditional medicine. Additionally, it's an important plant for beekeepers as it produces nectar-rich flowers, attracting pollinators.

Araucaria heterphylla
The Norfolk Island Pine, scientifically known as Araucaria heterophylla, is a distinctive evergreen tree native to Norfolk Island in the South Pacific. Despite its name, it's not a true pine but belongs to the Araucariaceae family. This tree is renowned for its symmetrical, tiered branches and dense, upward-pointing foliage, giving it a distinctive pyramidal shape, often resembling a Christmas tree. It can grow up to 200 feet (60 meters) tall in its natural habitat, but when cultivated as a houseplant, it typically remains much smaller.
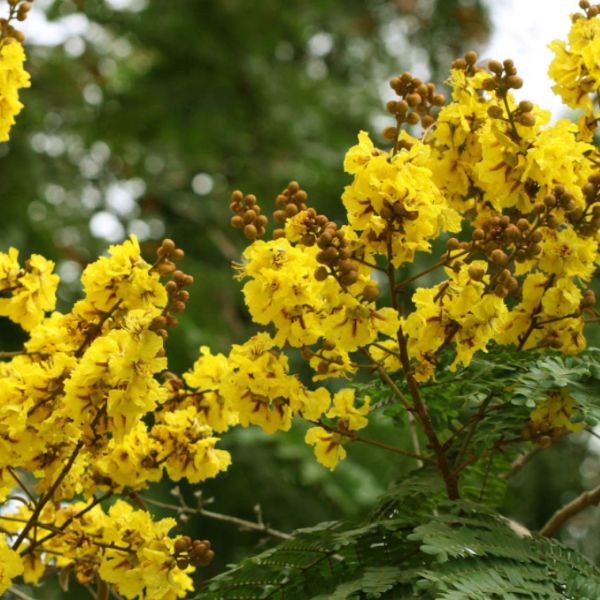

Peltophorum pterocarpum
The yellow flame tree, scientifically known as Peltophorum pterocarpum, is a striking and attractive tropical tree native to Southeast Asia, the Indian subcontinent, and northern Australia. It is known for its vibrant yellow flowers, which create a spectacular display when in full bloom.
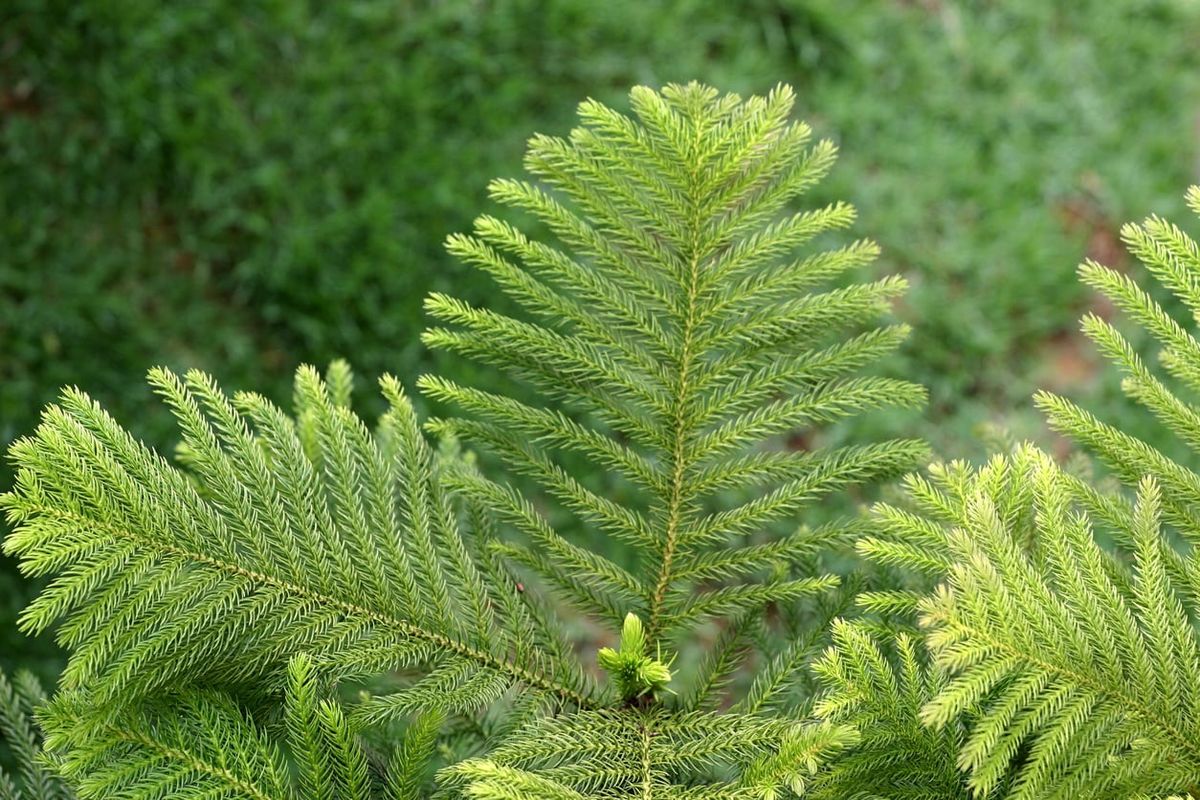

Araucaria heterphylla
The Norfolk Island pine, scientifically known as Araucaria heterophylla, is a distinctive and attractive coniferous tree native to Norfolk Island in the Pacific Ocean. Despite its common name and appearance, it is not a true pine.
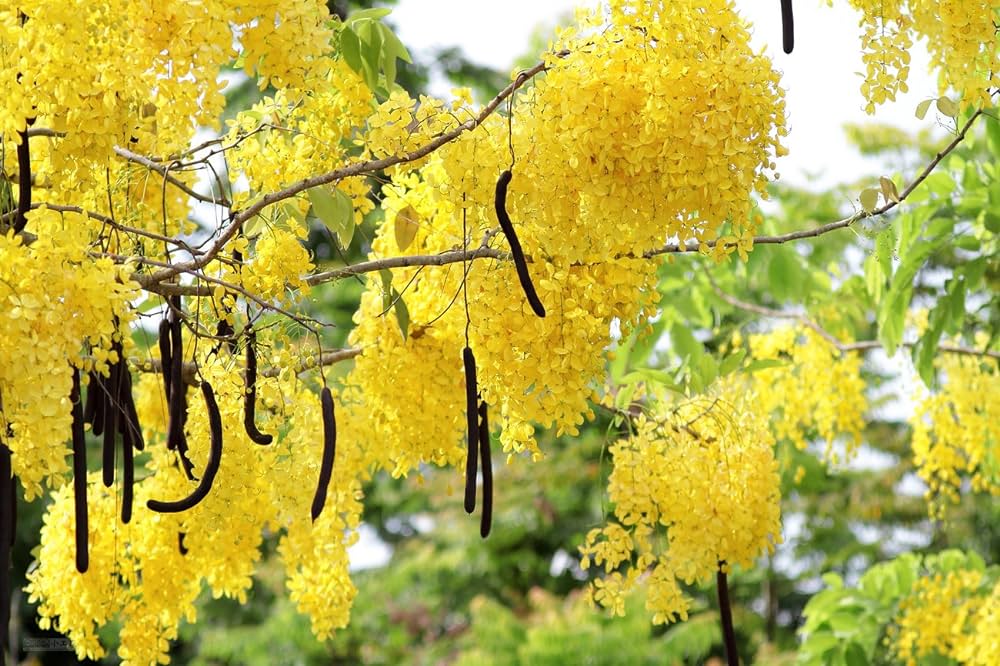

Cassia fistula
The golden shower tree, scientifically known as Cassia fistula, is a beautiful and highly ornamental tree native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. It is famous for its stunning display of bright yellow flowers.
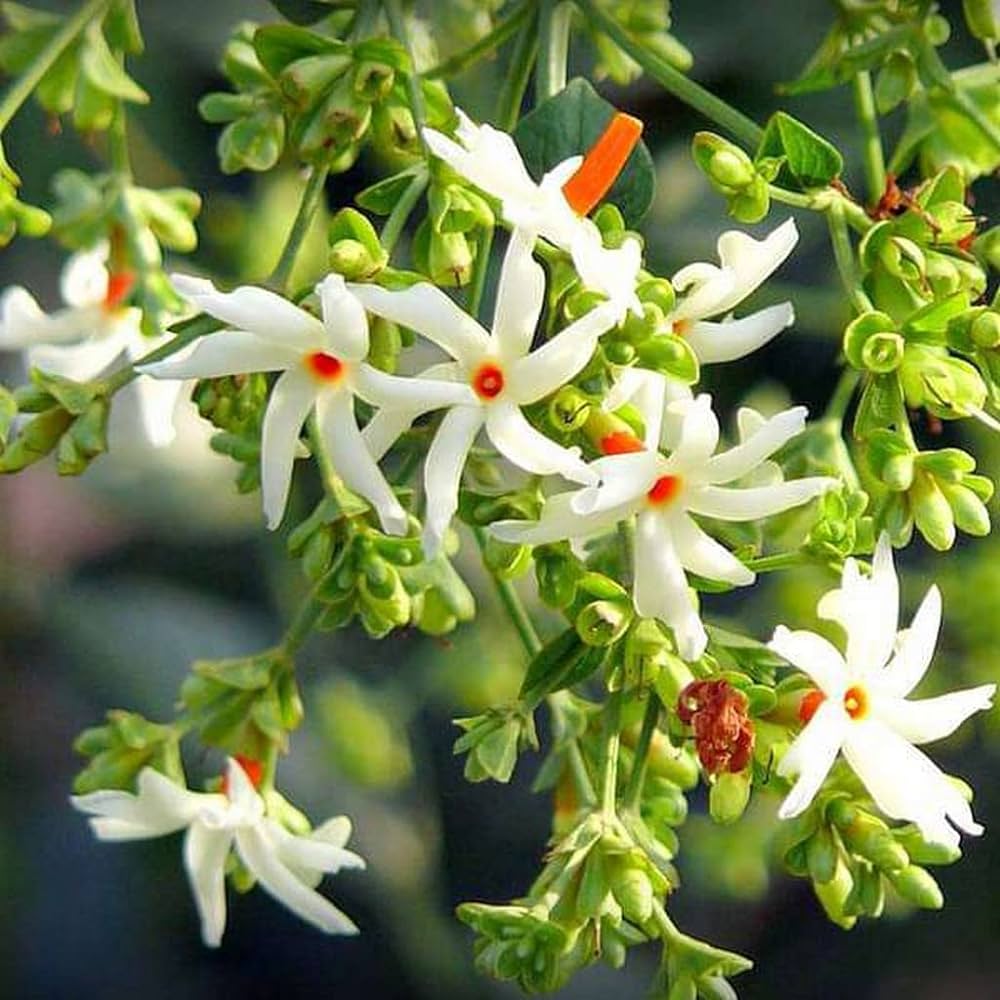

Nyctanthes arbor-tristis
Coral jasmine, scientifically known as Nyctanthes arbor-tristis, is a small, deciduous shrub or tree known for its fragrant, white flowers with orange centers. It is native to South Asia and Southeast Asia and is often grown for its ornamental and medicinal value.

Phyllanthus emblica
The amla tree, scientifically known as Phyllanthus emblica (also Emblica officinalis), is a deciduous tree renowned for its fruit, which is commonly known as Indian gooseberry. The tree is native to India and Southeast Asia and is highly valued for its medicinal properties and nutritional benefits.

Bauhinia purpurea
The orchid tree, scientifically known as Bauhinia variegata, is a deciduous tree native to Southeast Asia and widely cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions for its ornamental value. It is renowned for its large, showy flowers that resemble orchids, hence the common name.

Plumeria rubra
The frangipani tree, belonging to the genus Plumeria, is a small to medium-sized deciduous tree famous for its fragrant and beautiful flowers. It is native to Central America, the Caribbean, and parts of South America but is widely cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions around the world.
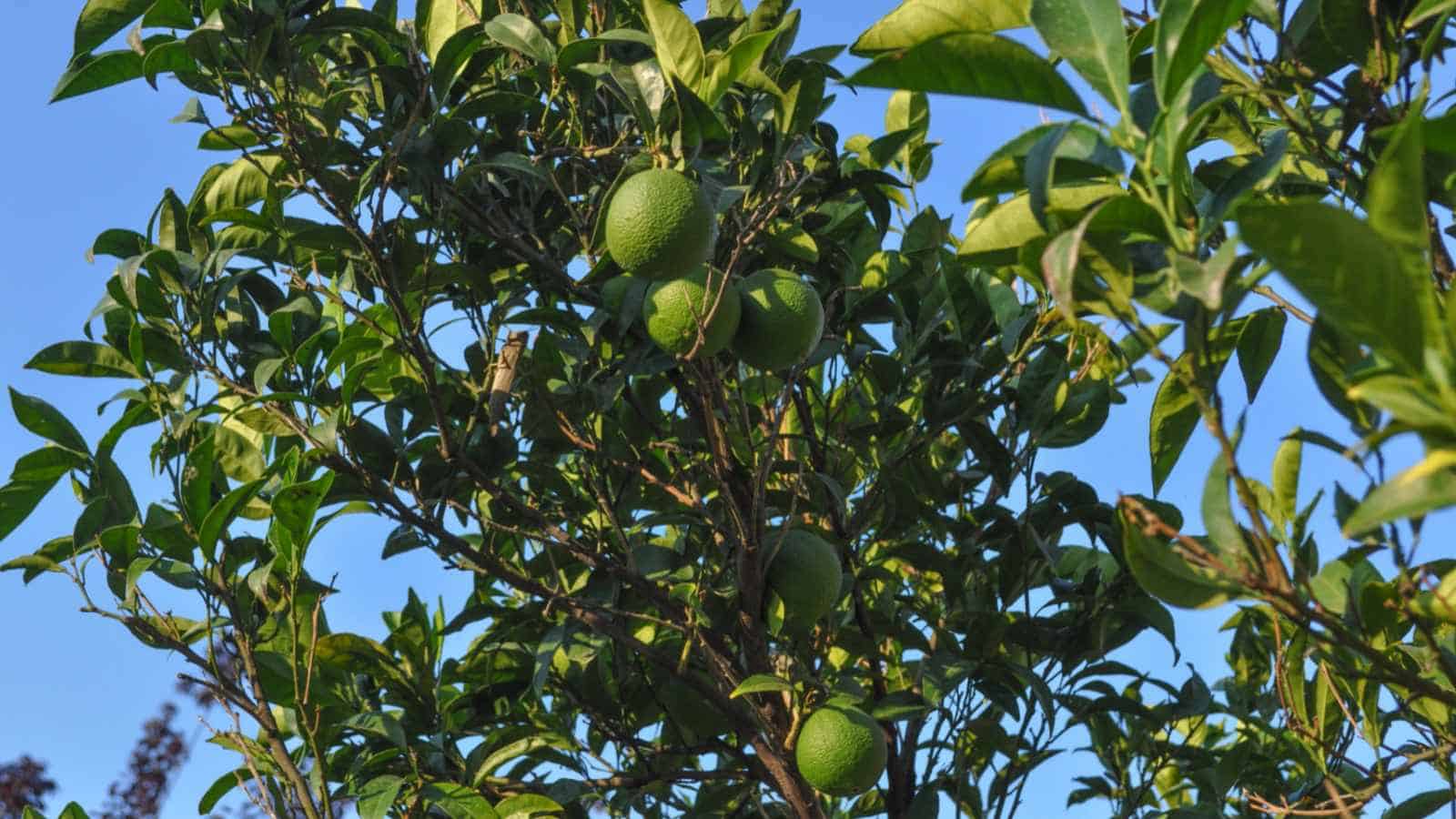

Citrus aurantifolia
The lime tree, scientifically known as Citrus aurantiifolia, is a small to medium-sized evergreen tree known for its small, green, acidic fruit. Native to Southeast Asia, it is now widely cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions around the world for its culinary and medicinal uses.

Albiza lebbeck
The Siris tree is a medium to large deciduous tree that can reach heights of up to 30 meters (approximately 100 feet). It has a spreading canopy with fern-like foliage, consisting of bipinnate leaves (meaning each leaf is divided into smaller leaflets, which are again divided into even smaller leaflets). The tree produces small, round, cream-colored flowers that are fragrant and attractive to pollinators like bees and butterflies.

Casuarilla equisetifolia
Coastal she-oaks are evergreen trees native to Australia, Southeast Asia, and various Pacific islands. They typically grow in coastal areas, often in sandy soils, and are well-adapted to salt spray and windy conditions. The foliage of coastal she-oaks consists of slender, green branchlets resembling pine needles. These branchlets are actually modified stems known as cladodes, which perform photosynthesis.
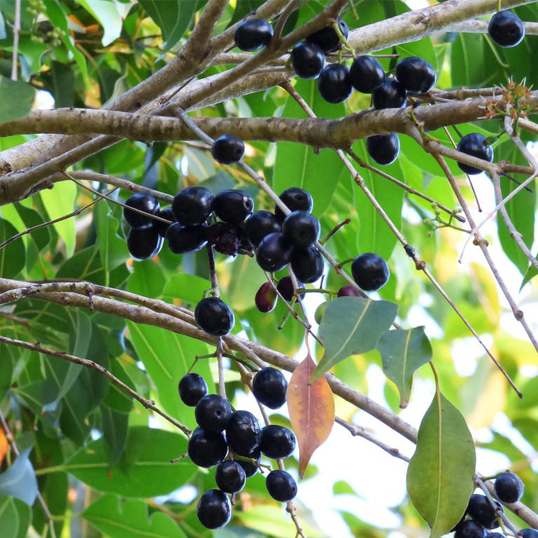

Syzygium cumini
The Jamun tree is a medium-sized evergreen tree that can grow up to 30 meters (approximately 100 feet) in height. It has a dense, spreading canopy with glossy, dark green leaves that are oblong or elliptical in shape. The tree produces small, fragrant, white or pink flowers in clusters, which later develop into fruit. The fruit of the Jamun tree is a berry-like drupe, usually purple or black when ripe, with a sweet and tangy flavor.
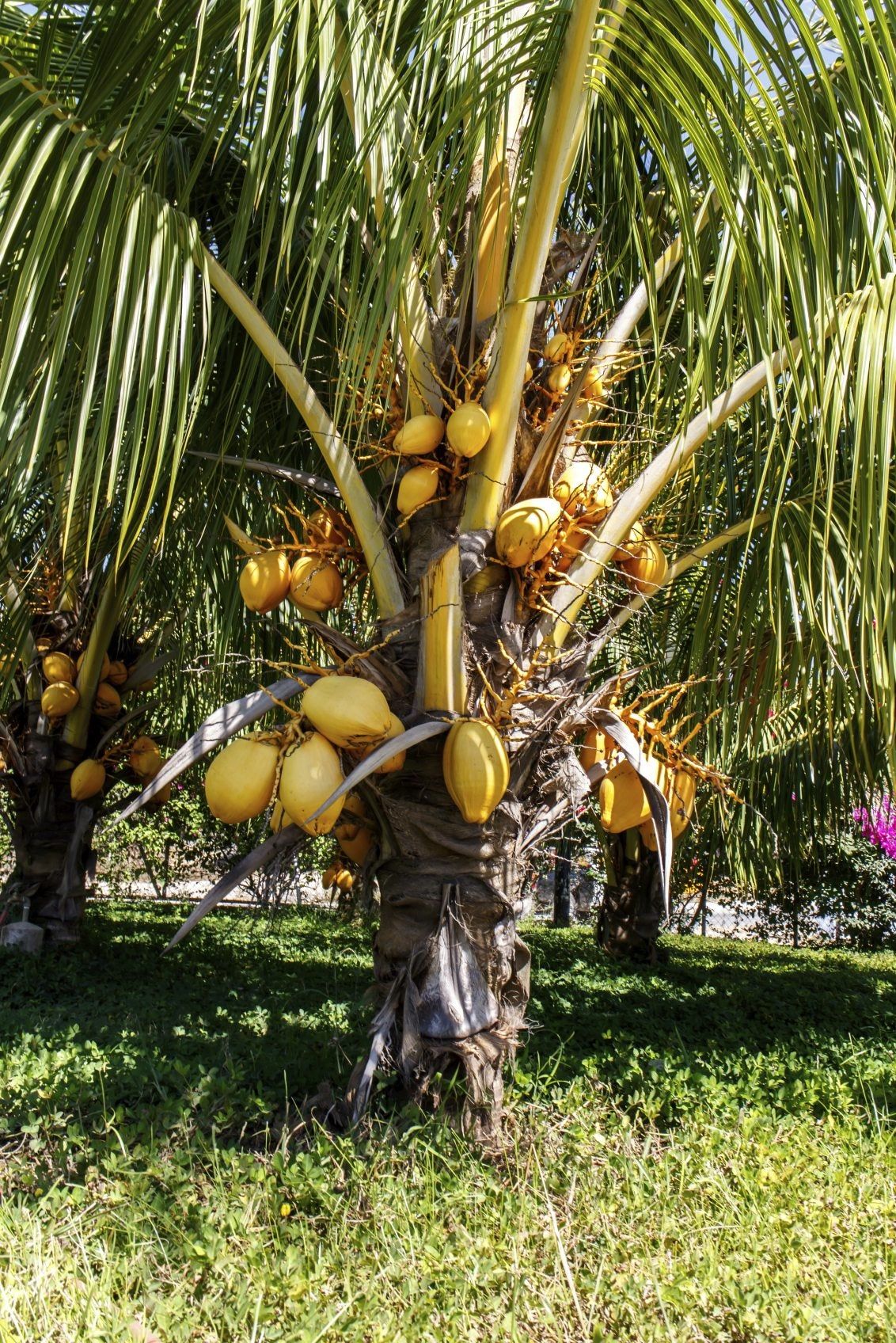

Cocos nucitera
The Coconut Palm is a tall, slender palm tree with a single, smooth trunk that can reach heights of up to 30 meters (approximately 98 feet). It has large, feather-like leaves that can grow up to 6 meters (20 feet) in length, arranged in a spiral pattern at the top of the trunk. The tree produces clusters of small, pale-yellow flowers that develop into coconuts. Coconuts are large, brown, fibrous fruits with a thick, hard outer husk, containing a single seed (the coconut) surrounded by a layer of edible, white flesh and a liquid known as coconut water.
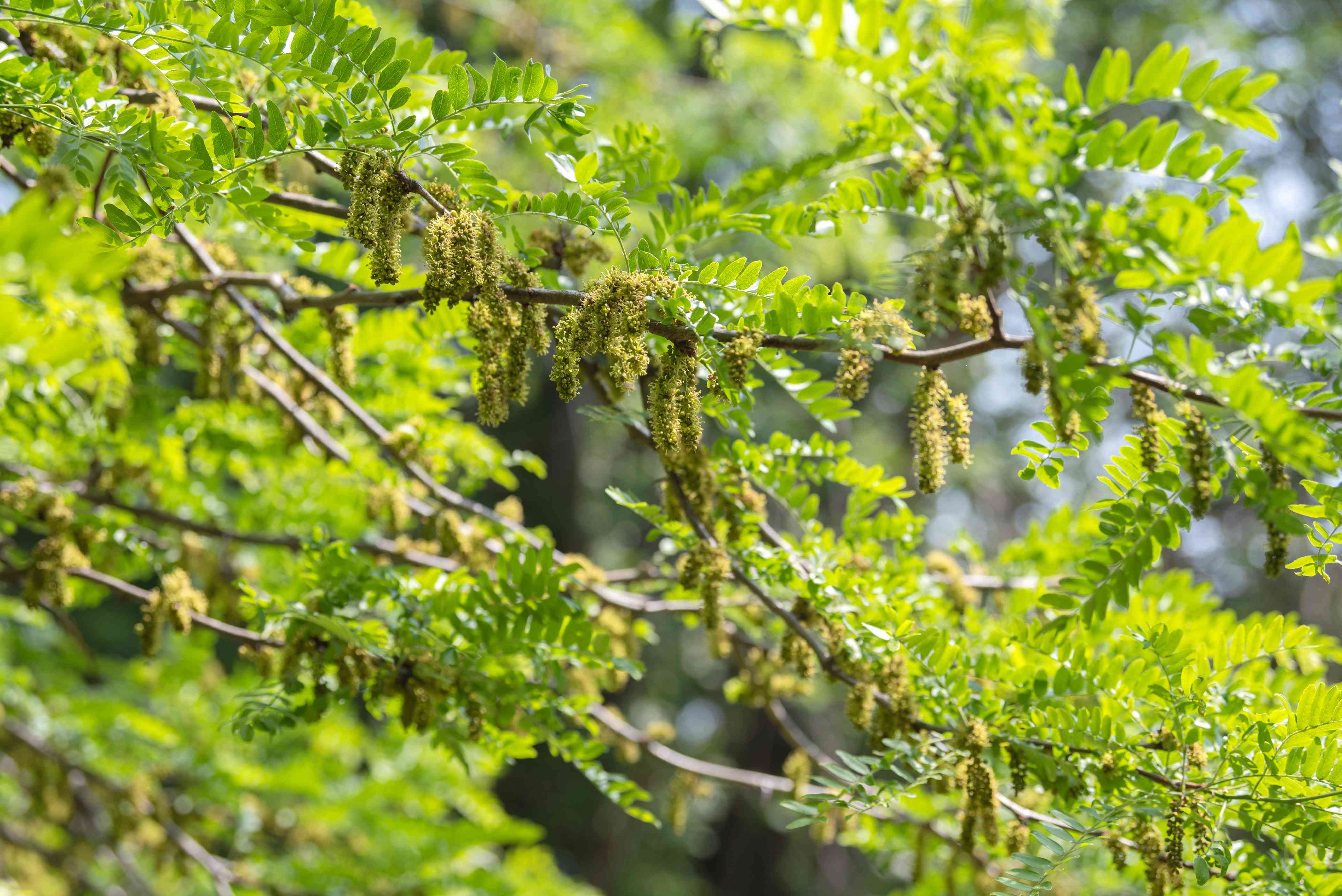

Gleditsia triacanthos
The Honey Locust is a medium to large-sized tree that can grow up to 20-30 meters (approximately 66-98 feet) in height. It has an open, spreading crown with compound leaves composed of numerous small leaflets. The tree produces fragrant, greenish-yellow flowers in spring, which are followed by long, twisted pods in the summer and fall. The pods of the Honey Locust contain seeds embedded in a sweet, sticky pulp, giving rise to the tree's common name, "Honey Locust."

Mangifera indica
The Mango Tree is a large, evergreen tree that can grow up to 30 meters (approximately 100 feet) in height, although cultivated varieties are often kept smaller for easier fruit harvesting. It has a dense canopy of dark green leaves, which are oblong or elliptical in shape and arranged spirally on the branches. The tree produces small, fragrant, white or pinkish flowers in clusters, which develop into fruit.
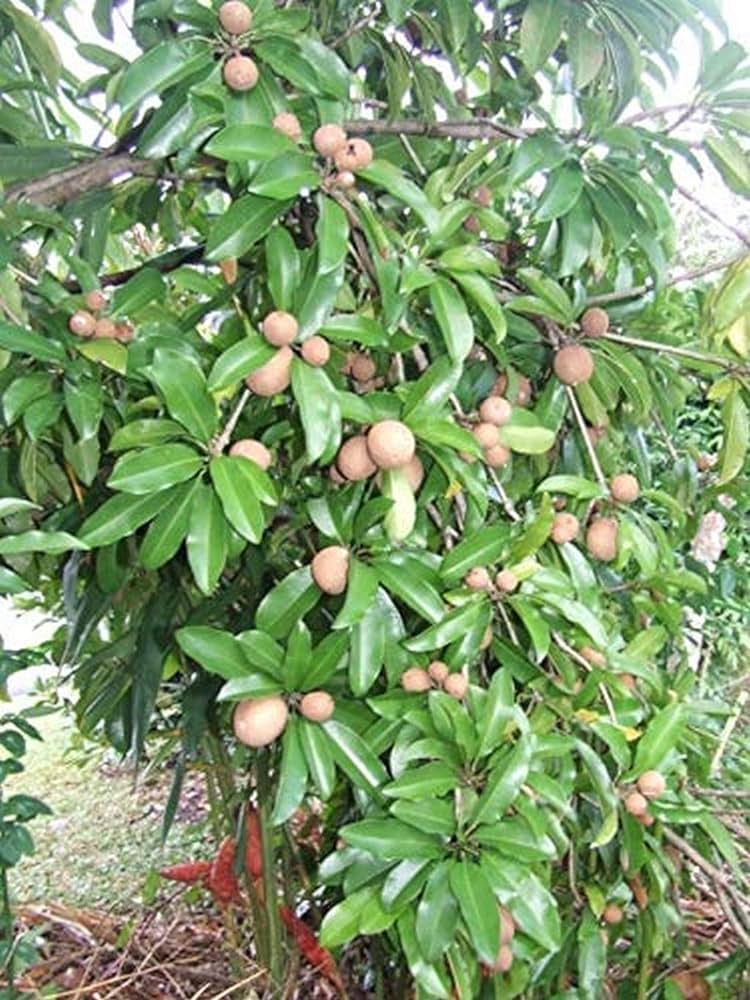

Manilkara zapota
It has glossy, leathery leaves that are elliptical or oblong in shape and arranged spirally on the branches. The tree produces small, inconspicuous flowers that are creamy-white or yellowish in color and are typically borne in clusters in the leaf axils.The fruit of the Sapodilla tree, also called Sapota or Chikoo, is an oval or round berry with rough, sandy brown skin when ripe. The flesh inside is soft, sweet, and aromatic, ranging in color from pale yellow to brown, depending on the variety and ripeness.
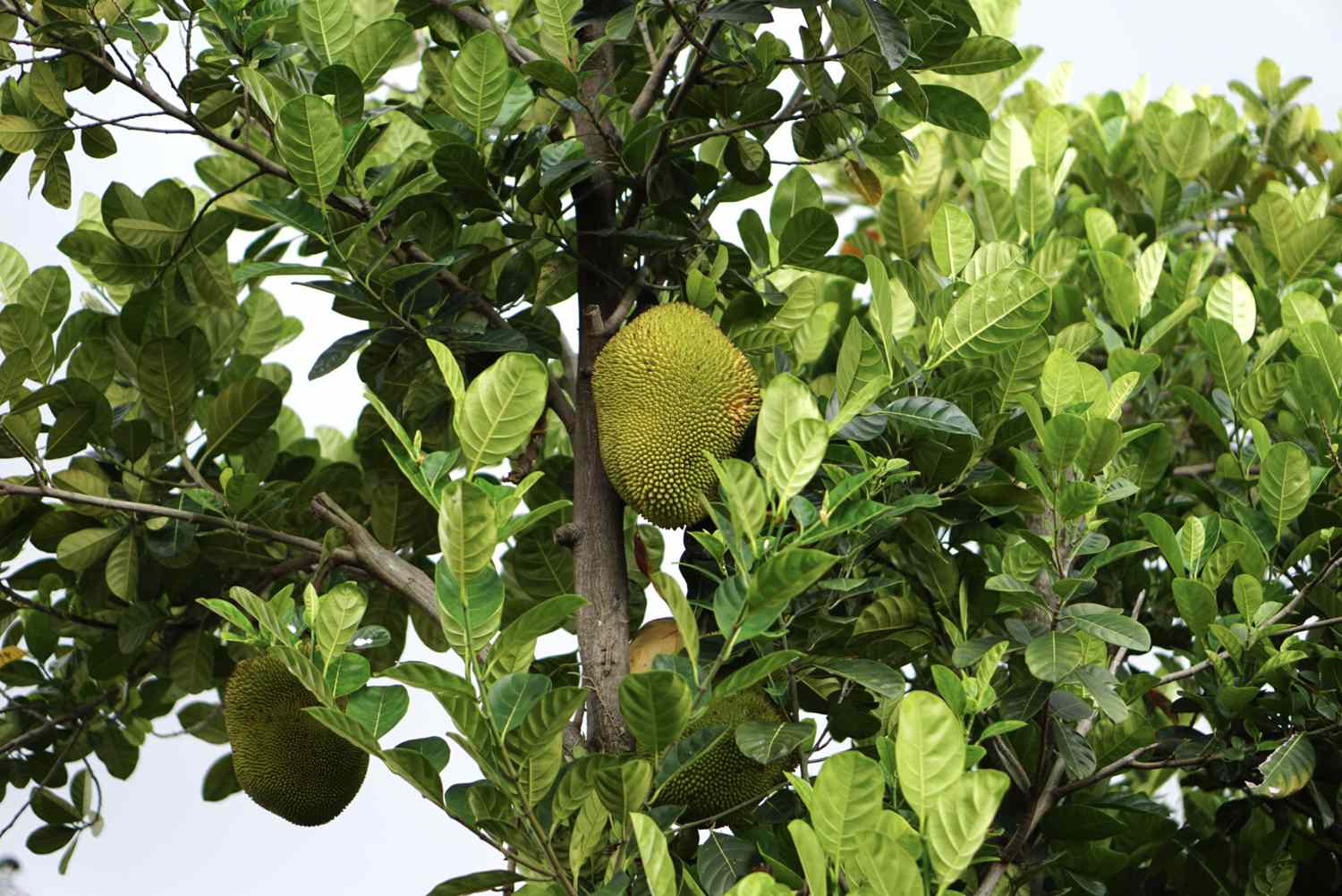

Artocarpus heterophyllus
The Jackfruit tree is a large evergreen tree that can reach heights of up to 20 to 30 meters (approximately 66 to 98 feet) with a spread of about 6 to 8 meters (approximately 20 to 26 feet). It has a dense canopy of glossy, dark green leaves that are alternate, oblong, and leathery in texture. The tree produces small, greenish-yellow flowers that are borne on thick, fleshy spikes on the trunk and branches.
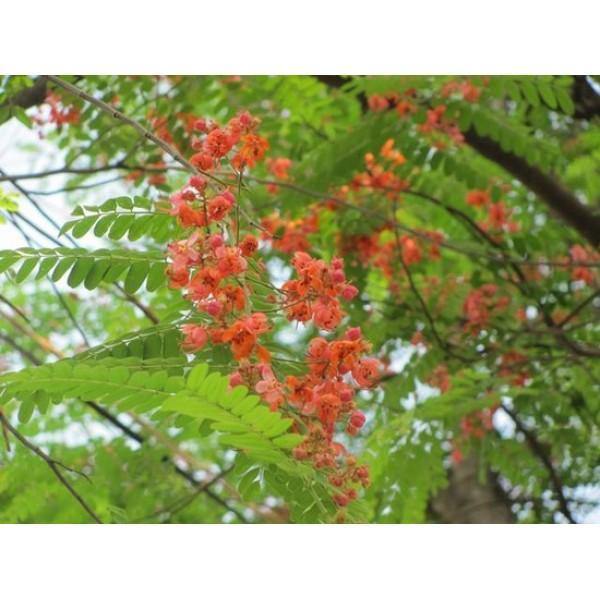

Cassia roxburghii
The Red Cassia tree is a medium to large-sized deciduous tree belonging to the Fabaceae family. It can reach heights of up to 25 meters (approximately 82 feet). It has a spreading canopy with compound leaves composed of several pairs of leaflets. The leaves are typically green and turn yellow before shedding. The tree produces showy clusters of bright pink to reddish-orange flowers, which appear in abundance during the flowering season. The flowers of the Red Cassia tree are typically bell-shaped and attract pollinators like bees and butterflies
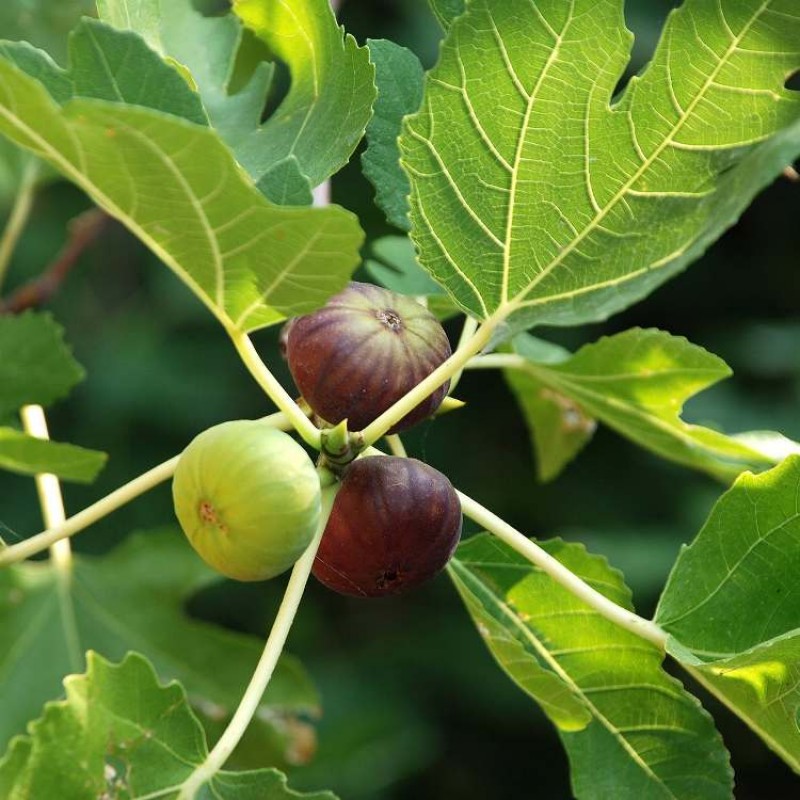

Ficus carica
The Fig tree is a small to medium-sized tree that typically grows up to 10-30 feet (3-9 meters) tall, although some cultivars can grow larger. It has large, lobed leaves that are rough to the touch and deeply veined. The leaves are typically green but may vary slightly in color depending on the variety. Figs are unique among fruit trees because their flowers are enclosed within a pear-shaped structure called a syconium, which later develops into the fruit.

Tectona grandis
The Teak tree is a large hardwood tree that can grow up to 30-40 meters (approximately 98-131 feet) tall, with a straight cylindrical trunk. It has large, oval-shaped leaves that are arranged oppositely on the branches. The leaves are typically dark green and have a rough texture. Teak trees produce small, white flowers that are arranged in dense clusters. These flowers are often inconspicuous. The wood of the Teak tree is highly valued for its durability, strength, and resistance to decay. It has a golden-brown to dark brown color and a straight grain, making it prized for a variety of applications.
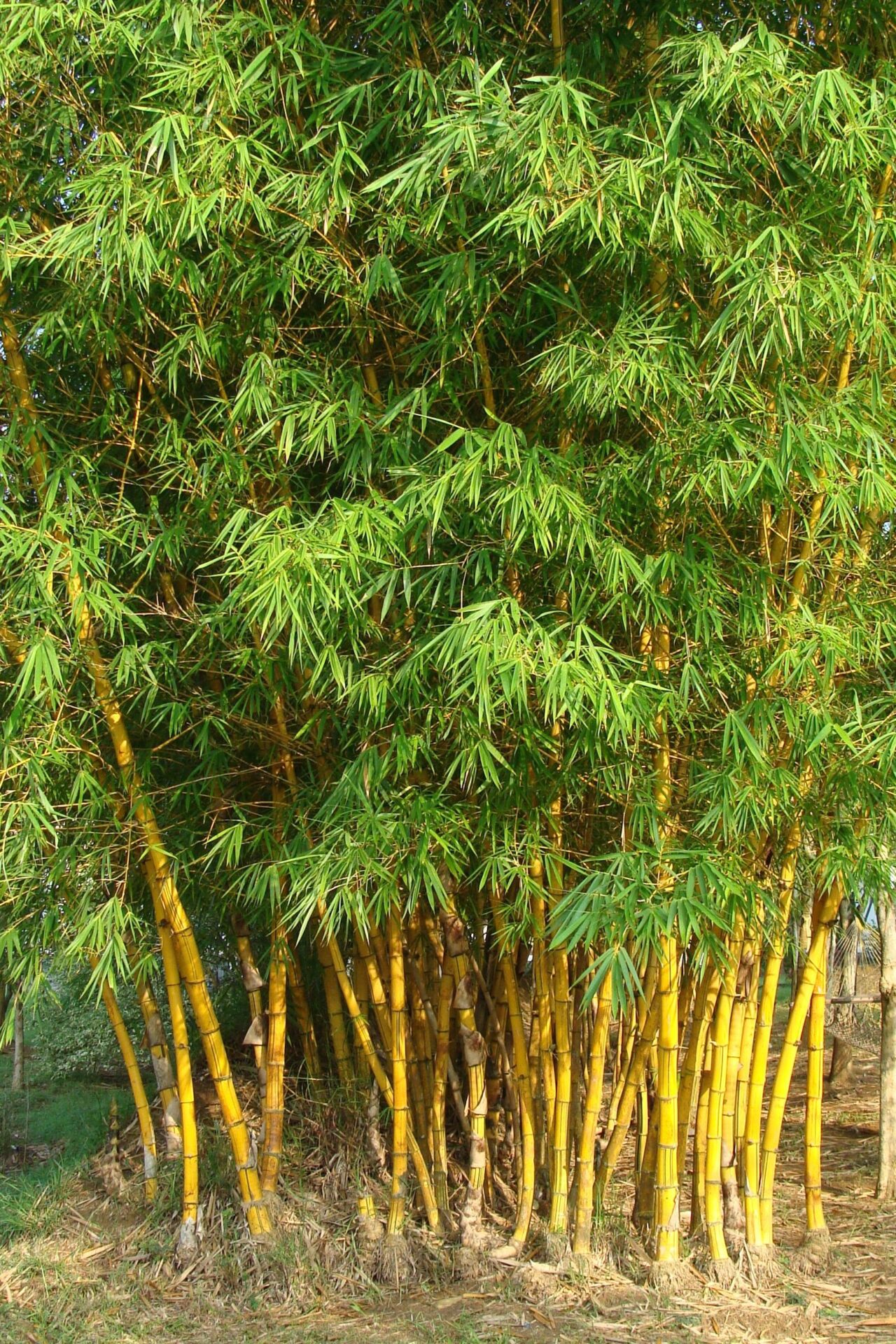

Bambusa vulgaris
Bamboo is characterized by its tall, upright, and hollow stems, known as culms, which can range in height from a few feet to over 100 feet (30 meters), depending on the species. The culms of bamboo are segmented by nodes, with leaves and branches emerging from these nodes. The leaves are typically long, narrow, and arranged alternately along the stems. Bamboo comes in various species and forms, including clumping and running varieties, with different sizes, colors, and growth habits.

Ficus benghalensis
The tree has broad, ovate leaves that are glossy green and leathery in texture. The leaves are arranged alternately on the branches. The aerial roots of the Indian Banyan tree grow from its branches and eventually reach the ground, where they take root and form new trunks, creating a characteristic maze-like structure. The fruit of the Indian Banyan tree is a small, spherical fig that starts green and turns purplish-black when ripe. These figs are an important food source for birds and other wildlife.
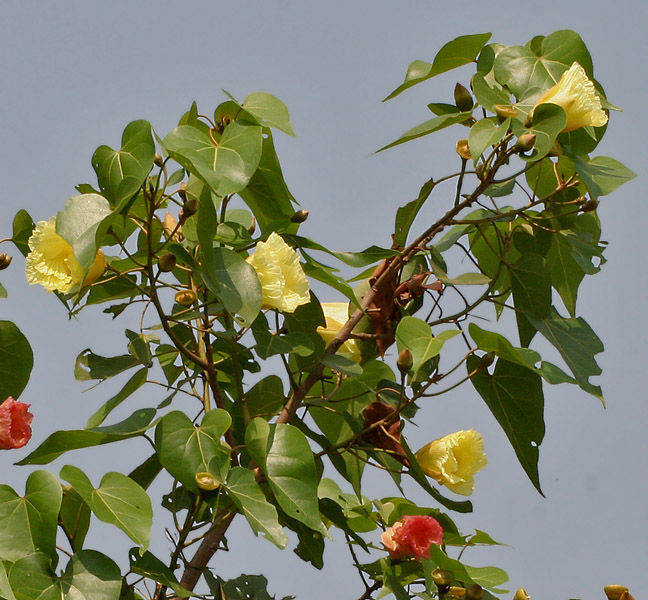

Thespesia populnea
The Indian Tulip Tree is a moderately sized tree that can grow up to 15-25 meters (approximately 49-82 feet) tall, with a broad, spreading canopy. It has large, heart-shaped leaves that are glossy green and arranged alternately on the branches. The leaves have prominent veins and toothed margins. The tree produces large, showy flowers that resemble tulips, hence its common name. The flowers are typically yellow with maroon or purple centers, although some varieties may have different color combinations
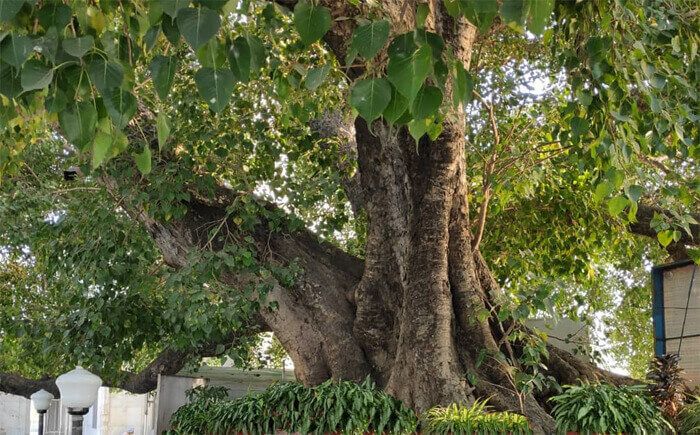

Ficus religiosa
It has heart-shaped leaves that are typically bright green and smooth on the upper surface, with a rough texture on the lower surface. The leaves are arranged alternately on the branches. The tree produces small, round figs that are green when immature and turn purple or black when ripe. These figs are an important food source for birds and other wildlife. The Peepal Tree is often associated with religious and cultural significance in various societies, particularly in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism.

Millingtona hortenis
Tree Jasmine is a medium to large-sized deciduous tree that can grow up to 20-25 meters (approximately 66-82 feet) tall. It has a straight trunk with a spreading canopy of branches and glossy, dark green compound leaves that are arranged alternately. The tree produces large, fragrant white flowers that resemble jasmine flowers, hence its common name. These flowers are borne in terminal clusters and have long, tubular corollas with five petals.The flowers of Tree Jasmine typically bloom during the spring and summer months, filling the air with a sweet, floral fragrance.

